3D printing does not make items by cutting or moulding them like traditional manufacturing machines. The method of forming physical objects by stacking them in layers expands the scope of the digital concept from a physical point of view. For shape designs that require precise internal dimpled or interlocked parts, 3D printing is the preferred processing device, which can implement such designs in the physical world.
Here are people from various industries, with different backgrounds and levels of expertise, describing in similar ways how 3D printing has helped them reduce major cost, time and complexity barriers. Let’s take a look at the advantages of 3D printing.
What is 3d printing rapid Prototyping technology
What is 3d Printing technology? To be exact, 3D rapid prototyping technology is one of the many rapid prototyping technology, rapid prototyping technology can be roughly divided into seven categories, including three-dimensional printing, laminated solid manufacturing, selective laser sintering, melt deposition molding, three-dimensional welding, three-dimensional printing, digital accumulation molding.
3d printing technology process principle
With the continuous development of various 3D printing technologies, many industries have adopted a variety of 3D printing technologies, including: electron beam melting, melt deposition modeling, layered solid manufacturing, three-dimensional printing, stereolithography modeling, selective laser sintering. The following is the process principle of these six technologies, see the text for details.
Electron beam melting (EBM)
EBM technology is an emerging advanced metal rapid prototyping additive manufacturing (form additive manufacturing) technology that uses an electron beam instead of a laser or thermal printhead. The electron beam melting process is often used to make incredibly dense metal parts.
Process principle:
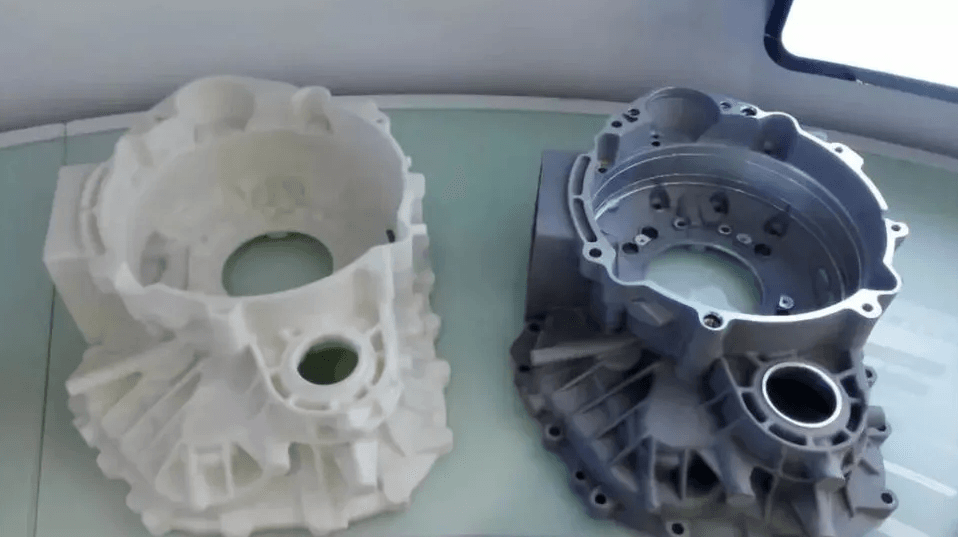
First, the 3D solid model data of the parts are imported into the EBM equipment, and then a thin layer of fine metal powder is laid out in the working chamber of the EBM equipment. The high-density energy generated by the high-energy electron beam after deflection and focusing is used to make the scanned metal powder layer produce high temperature in the local tiny area, resulting in the melting of the metal particles. The continuous scanning of electron beams will make a tiny metal melt pool fuse with each other and solidify, and form a linear and planar metal layer after joining.
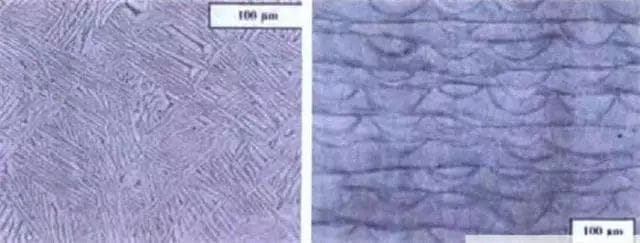
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
This is an additive manufacturing (AM) technology that is commonly used in modeling, prototyping, and production applications. This 3D printing technology was developed by American scholar Scott Crump in 1988. Generally speaking, FDM is the use of high temperature to melt the material into a liquid state, through the printing head after extrusion curing, and finally arranged on the three-dimensional space to form a three-dimensional object.
Process principle:
The filament-like material with low melting point is melted into a liquid through the extrusion head of the heater, the melted thermoplastic material is extruded through the nozzle, the extrusion head moves accurately along the profile of each section of the part, extrudes the semi-flowing thermoplastic material, deposits and solidifies to form a precise thin layer of the actual part, which covers the built part, and quickly solidifies within 0.1 seconds. After each layer of molding is completed, the workbench drops a layer of height, and the nozzle scans the section of the next layer, so that the layer by layer deposition, until the last layer, so that the layer by layer from the bottom to the top pile up into a solid model or part.
Layered physical Manufacturing (LOM)
Also known as cascade forming, it was developed by Michael Feygin of Helisys in 1986.
Process Principle:
It uses thin sheet materials, such as paper, plastic film, etc. In advance, a layer of hot melt adhesive is coated on the surface of the sheet. During processing, the sheet is hot pressed by a hot press roller to make it bond with the formed workpiece below. A CO2 laser is used to cut the cross section outline of the part and the outer frame of the workpiece on the newly bonded layer, and the mesh is cut out in the excess area between the cross section outline and the outer frame. After the laser cutting is completed, the table drives the formed workpiece down and separates it from the strip sheet (material belt); The feeding mechanism rotates the receiving shaft and the feeding shaft to drive the material belt to move the new layer to the processing area; The table rises to the machining plane; The number of layers of the workpiece is increased by one layer, and the height is increased by one material thickness. Then cut the section outline on the new layer. This is repeated until all sections of the part are bonded and cut to obtain a solid part manufactured in layers.
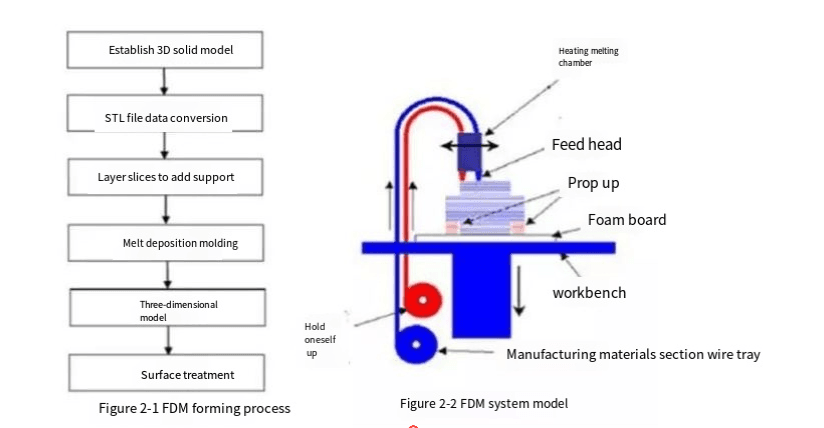
3D printing
Similar to traditional 2D inkjet printing, it can print ultra-fine samples and is suitable for rapid prototyping of small fine parts.
Process principle:
Slide back and forth along the X-axis to lay an ultra-thin layer of photosensitive resin in the molding chamber. After each layer is laid, the ultraviolet ball on the side of the nozzle frame immediately emits ultraviolet light to quickly cure and harden each layer of photosensitive resin. This step reduces the post-processing required to use other technologies. After each layer is printed, the molded chassis inside the machine sinks with extreme precision, and the nozzle continues to work layer by layer until the prototype is complete. Two different kinds of photosensitive resin materials are used in the molding: one is the molding material used to form the solid parts, and the other is the colloidal support material used to support the parts.
Stereolithography modeling
High precision stereolithography modeling, can show accurate surface and smooth effect, accuracy can reach 0.05 mm to 0.15 mm per layer thickness.
Process principle:
First, the software “cuts” the 3D digital model into several planes, which forms many profiles. When working, there is a platform that can be lifted, and there is a liquid tank around the platform, which is filled with liquid that can be cured by ultraviolet radiation. The ultraviolet laser will start from the bottom, cure the bottom layer, and then the platform will move down to cure the next layer. And so on, until the final shape.
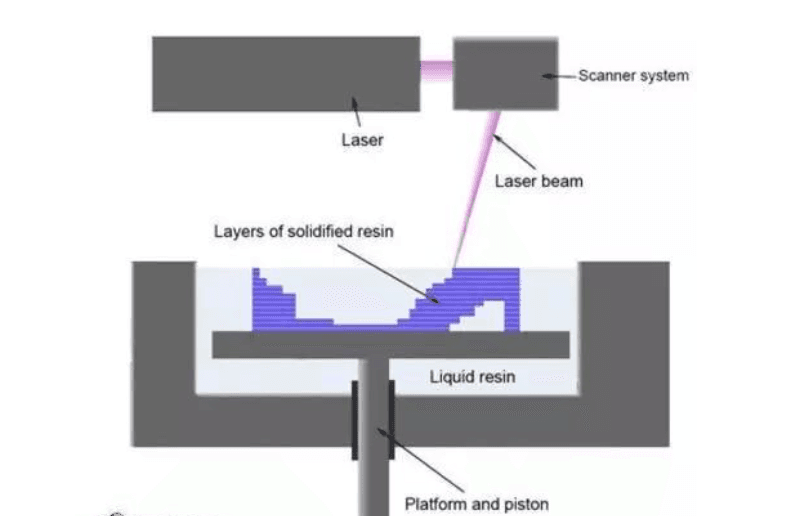
Selective laser Sintering (SLS)
The strength of the material is very high, and the optional materials range from metal to polystyrene and so on.
Process principle:
After the 3D model is laminated, it is filled with material powder to be sintered in a container, which can be made very fine, and then the bottom 3D slice shape is selected by a high-power carbon dioxide laser to start sintering, and then the platform is moved down, and the material roller is laid on the foundation of the sintered part, and then a thin layer of material powder is sintered, and so on. Until the whole thing is formed.
Advantages of 3D printing
In contrast to CNC machining, which uses subtractive manufacturing, additive manufacturing adds materials in layers until the product is finished. The use of 3D printers has many benefits for both large businesses and individuals.
Advantage 1: Manufacturing complex items does not add cost
As far as traditional manufacturing is concerned, the more complex the shape of the object, the higher the manufacturing cost. For 3D printing, the cost of manufacturing complex shaped items does not increase, and creating a gorgeous complex shaped item does not take more time, skill or cost than printing a simple square. Making complex items without adding cost will disrupt traditional pricing models and change the way we calculate the cost of manufacturing.
Advantage 2: Product diversification does not increase costs
3D printing can print many shapes, and it can make different shaped items each time like a craftsman. Traditional manufacturing equipment has fewer functions and can produce a limited variety of shapes. Instead of training mechanics or buying new equipment, 3D printing requires a different digital design blueprint and a new batch of raw materials.

Advantage 3: Zero skill manufacturing
Traditional craftsmen need to apprentice for several years to acquire the skills they need. Mass production and computer-controlled manufacturing machines reduce the skill requirements, however traditional manufacturing machines still require skilled professionals to make machine adjustments and calibrations. 3D printing gets various instructions from the design file, and to make the same complex items, 3D printing requires less operating skills than the injection molding machine. Unskilled manufacturing opens up new business models and offers people new ways to produce in remote environments or in extreme situations.
Advantage 4: No assembly required
3D printing has the characteristics of one-piece forming, which has a significant help in reducing labor and transportation costs. Traditional mass production is based on industrial chains and assembly lines, in modern factories, machines produce the same parts, which are then assembled by workers. The more components a product has, the longer the supply chain and product line will stretch, and the more time and cost it will take to assemble and ship. The 3D printing integrated forming features, no need to assemble again, thereby shortening the supply chain, saving on labor and transportation costs.
Advantage 5: Zero time delivery
3D printing can be printed on demand. Instant production reduces the physical inventory of enterprises, enterprises can use 3D printing to manufacture customized parts according to customer orders to meet customer needs, so new business models will become possible. If the goods people need are produced nearby as needed, zero-time delivery production can minimize the cost of long-distance transportation.
Advantage 6: Unlimited design space
Traditional manufacturing techniques and artisans make products in limited shapes, and the ability to make shapes is limited by the tools used. For example, traditional wooden lathes can only make round items, rolling mills can only process parts assembled with milling cutters, and molding machines can only make molded shapes. 3D printing can break through these limitations, opening up huge design Spaces and even making shapes that may currently only exist in nature.
Advantage 7: Unlimited combination of materials
It is difficult for today’s manufacturing machines to combine different raw materials into a single product, because traditional manufacturing machines cannot easily combine multiple raw materials during cutting or mold forming. With the development of multi-material 3D printing technology, we have the ability to fuse different raw materials together. Raw materials that could not be mixed before will be mixed to form new materials, which have a wide variety of shades and have unique properties or functions.
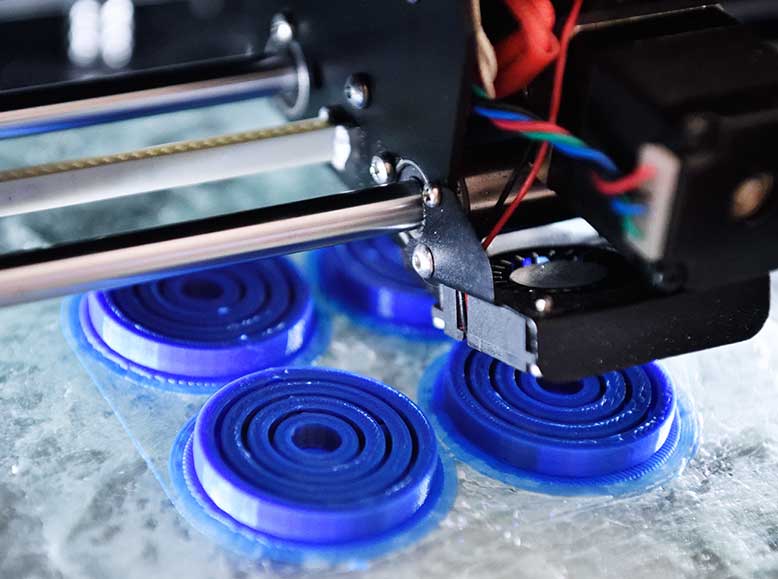

Advantage 8: No space, portable manufacturing
In terms of unit production space, the manufacturing capacity of 3D printing is stronger than that of traditional manufacturing machines. For example, an injection molding machine can only make items much smaller than itself, in contrast to a 3D printer that can make items as large as its printing table. After the 3D printer is adjusted, the printing equipment can move freely, and the printer can make items larger than itself. The high production capacity per unit of space makes 3D printers suitable for home or office use because of the small physical space they require.
Advantage 9: Accurate physical replication
Digital music files can be copied endlessly without any degradation in audio quality. In the future, 3D printing will extend digital precision to the physical world. Scanning technology and 3D printing technology will work together to increase the resolution of morphological transformations between the physical and digital worlds, allowing us to scan, edit and copy physical objects to create exact copies or optimize originals.
Advantage 10: Reduce waste by-products
Compared to traditional metal manufacturing techniques, 3D printers produce fewer by-products when making metal. The amount of waste in traditional metal machining is staggering, with 90% of metal raw materials discarded on the factory floor. Less waste when 3D printing makes metal. With advances in printing materials, “net forming” manufacturing could become a greener way to process.
Of course, 3D printing not only has advantages, but also has disadvantages. The following points are the disadvantages reflected in the application of 3D printing technology. With the advancement of technology and corresponding research results, these conditions are expected to improve in the future.
Whether the finished product is strong and durable
Houses and cars can be “printed” out, but can they withstand the wind and rain and run smoothly on the road? 3D printing is currently more commonly used polymer materials, and each material has its own melting point and various properties such as fluid, 3D printing is difficult to achieve the current combination of various materials, resulting in printed products brittleness and other shortcomings.
It is difficult to overcome environmental factors
In the 3D printing room, usually due to insufficient air purification, gaps in the machine, and impurities mixed in the metal powder material, the chemical composition of the part may change.
conclusion
The ownership of 3D printers has grown to the point where only a handful of companies don’t have the technology. Even though 3D printers are easier to use than ever before, some companies are unable to purchase 3D printers for a variety of reasons. 3D printing services, such as 3D hubs, offer an alternative to owning a 3D printer. Longsheng is a company specializing in the production of 3D printed parts. More than 3 million parts are produced and shipped worldwide. The process is quick, simple and economical.


