Standing in the window of the LS Materials Lab, I observe firsthand daily how high-density polyethylene (HDPE) quietly works its magic, reshaping the world around us. This fairly unassuming white plastic sheet never fails to amaze me with its phenomenal performance and multifarious applications. HDPE sheet at LS is not just a raw material; it is the master key that engineers use to unlock tough challenges.
The durable cutting board on your kitchen counter, the inside of a city pipe that provides clean water for years, even the climbing walls children romp on in the park—at the heart of all these applications, the HDPE sheet we select so meticulously is most likely working overtime. Its unparalleled durability withstands impact, its superior chemical resistance withstands a wide variety of solvents and harsh conditions, and its superior value provides the perfect balance of reliability and cost.
We at LS recognize the basic value of HDPE sheet: it’s a fantastic substrate for custom fabrication and a reliable source for high-volume standard parts. Whether it requires on-site cutting, welding, or bending into specific shapes (such as enormous tank linings and wear-resistant linings) or as the focal material for cleanroom worktops and food processing conveyor belts, HDPE sheet provides an indispensable solution. However, in the face of the requirement for huge, complicated parts, a moment of reckoning arrives: to keep utilizing sheet for secondary processing or move on to the more efficient process of injection molding. This is our key topic that we will be discussing in depth. Having an insight into the limits and horizon of HDPE sheet will guide us in making the most informed manufacturing choices.
Core Applications and Characteristics of HDPE Plastic Sheet
| Core Applications | Specific Product Examples | Key Features Utilized | Primary Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing and Handling | Commercial cutting boards, food containers, butcher blocks, conveyor belt liners | FDA food-grade safe, non-porous (inhibits bacterial growth), moisture-resistant and non-deformable, smooth and easy-to-clean surface, wear-resistant | Sheet cutting, thermoforming, injection molding |
| Chemical Storage and Transportation | Chemical storage tanks, tank linings, laboratory workbenches, pipe linings | Excellent acid, alkali, solvent, and corrosion resistance, high purity, low adsorption, and resistance to chemical swelling | Sheet welding (hot melt/extrusion), rotational molding |
| Construction and Civil Engineering | Water supply/sewage pipes, geomembranes, landfill linings, bridge bearing sliders | Good flexibility, high impact resistance, excellent weather resistance (anti-UV aging), ultra-long service life, chemical inertness, low friction coefficient | Extrusion molding (pipes/profiles), sheet welding (membranes/linings), pressing and sintering (large sheets) |
| Entertainment and Consumer Goods | Children’s playground equipment (slides), stadium seating, marine accessories (fenders, rails), ski bottoms. | UV resistant (additives required), excellent wear resistance, high impact strength, safe and non-toxic, self-lubricating, low water absorption. | Roto-molding, sheet metal processing (cutting/milling/hot bending), press sintering. |
| Industrial manufacturing | Machine guards, conveyor belt components (sprockets/guide rails/scrapers), packaging materials (pads/silo linings), gears, bearings | Extremely high impact strength (better than steel), extremely low coefficient of friction (self-lubricating), wear resistance (better than carbon steel), easy processing, chemical resistance, and low noise. | Sheet metal CNC machining, injection molding, press sintering, and extrusion. |
Here’s What You’ll Learn:
- Five core application areas—from the food industry to marine engineering—precisely match the irreplaceable nature of HDPE sheet.
- A pragmatic answer to chemical tank linings—a how-to on 10-fold corrosion resistance for 1/3 the price using HDPE.
- Three key specifications for UV-resistant marine sheet–three acceptance criteria to prevent material failure pitfalls.
- The secrets of medical-grade HDPE molding—high-strength thermal balance control technology and biocompatibility.
- Choosing sheet processing versus injection molding—make the decision in an instant based on production volume, complexity, and cost.
- The truth behind environmental row—carbon emissions data and recycling economy plans of Recycling Code 2.
Break open this definitive guide to industrial-grade plastics today and give your projects a commanding edge.
What is HDPE Plastic All About?
HDPE, or high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is a thermoplastic whose molecules have a tightly packed, tightly packed chain with minimal branching. Its unique molecular structure gives it high density and crystallinity and thus higher hardness, tensile strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability than its branched counterpart, low-density polyethylene (LDPE, which can be found in plastic wrap). HDPE is, briefly, a hard, semi-rigid plastic substance with a high strength-to-weight ratio.

The Top 5 Applications of HDPE Sheets
HDPE sheet, with its perfect processing characteristics (easy to cut, weld, and drill) and excellent material characteristics, has proven itself to be widely applicable in various industries. Below is an overview of its five main application areas:
| Application Area | Specific Application | Core Advantages/Features | Related Standards/Grades |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Industry | Cutting Boards, Countertops | Non-cracking, non-bacterial, easy to clean | FDA and NSF compliant |
| Chemical Anti-corrosion | Tank Linings (concrete/steel) | Excellent corrosion resistance, cost-effective | – |
| Marine Engineering | Cabin Doors, Deck Accessories, Fishing Rod Holders | Saltwater-corrosion and UV-resistant, no rotting or delamination | Marine Grade (UV-resistant treatment) |
| Industrial Protection/DIY | Machine Guards, Fences, Baffles | Impact-resistant, easy to form | – |
| Medical Devices | Orthopedic braces , Prosthetic parts | Lightweight, high strength, biocompatible, thermoformable | Medical grade |
- Food Industry: HDPE is an ideal material for cutting boards and commercial kitchen countertops. Crack resistance, bacteria absorbency, and cleanliness are all in full compliance with demanding food contact safety standards (FDA/NSF).
- Chemical Corrosion Protection: Welding HDPE sheet to the interior of large storage tanks as linings is a cost-effective and effective means of protection, resisting many corrosive chemicals and prolonging tank life significantly.
- Marine Engineering: HDPE sheet of high density with marine grade UV resistant coating is widely used in the manufacturing of various ship components due to better weather resistance (no rot, delamination, or color change) under harsh saltwater conditions.
- Industrial Protection and DIY: The excellent impact resistance and workability (cutting, drilling, and bending) of HDPE sheet make it extremely sought after as protective equipment such as machine guards, sports field fencing, and baffles, and for DIY uses.
- Medical Devices: Thermoformable medical-grade HDPE sheet can be specially molded into light, high-strength, and biocompatible orthopedic braces and prosthetic parts, meeting the needs of the medical rehabilitation industry.
The easy processing and versatility of HDPE sheet make it a common high-performance material in a wide range of contexts from kitchens and chemical factories to the ocean and clinics.
Key Properties That Make HDPE Highly Versatile
Its wide range of uses for high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is attributed to the unique and well-balanced list of key physical and chemical properties. These qualify it as an adequate material for most industrial, packaging, and consumer processes.
HDPE Key Properties and Application Value Quick Reference
| Key Properties | Application Value |
|---|---|
| Excellent Chemical Resistance | Resists corrosion from acids, alkalis, alcohols, and detergents, making it suitable for chemical containers and piping. |
| High Impact Strength | Resists impact at low temperatures and offers durability, making it suitable for use in turnover boxes, outdoor equipment, and ice buckets. |
| Extremely Low Hygroscopicity | Does not absorb water and offers dimensionally stable properties, making it suitable for use in humid environments, water storage containers, and piping. |
| High Tensile Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio, lightweight yet strong, making it suitable for use in large containers, films, and ropes. |
| Easy Welding and Processing | Strong hot air welding and easy CNC machining facilitate fabrication, joining, and forming. |
| Food Grade Safety | Compliant with FDA standards, safe for food contact, making it suitable for use in food packaging, cutting boards, and drinking cups. |
- Chemical Resistance: HDPE is also an efficient anti-corrosion chemical inhibitor against a wide range of chemicals and a preferred material for safe piping and containers for chemicals storage and transportation, cleaning agents, and domestic chemicals.
- Impact Resistance: Inspite of low temperatures, HDPE resists severe impact without breaking and is therefore highly resistant and particularly favorable to application where exposure to exterior forces or low temperatures occurs.
- Low Water Absorption: HDPE absorbs very little water, ensuring its long-term size and shape stability in water-rich or humid conditions. It is an apt material to use in containers for keeping water, underground pipes, and sealed packages with moisture.
- Tensile Strength: Due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, it needs less material to achieve the desired strength, satisfying lightness and toughness in equipoise. It is widely used in enormous industrial tanks, films, and load bearings.
- Processability: Its excellent hot-air welding characteristic ensures firm joints, whereas its superior CNC machinability enhances production and design convenience to a great extent, enabling the easy manufacture of complex parts.
- Food Safety: Virgin HDPE meets rigorous food safety standards and is suitable for direct food contact and drinking water contact. It is widely and trustworthy applied in food packaging, kitchenware, and drinking water machines.
All in all, it is this combination of high strength and toughness, corrosion resistance, moisture absorption resistance, easy processability, safety, and reliability that has led to HDPE’s widespread and invaluable application becoming a part of contemporary society.

HDPE Sheet vs. Injection Molding: Which is Right for You?
Main decision criterion: Your part shape complexity and series volume determine the optimal process.
| Features | HDPE Sheet Fabrication | HDPE Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable shapes | Large, flat, simple 2D shapes | Complex 3D geometries (ribs, clips, holes, etc.) |
| Production Volume | Ideal for rapid prototyping, small batches (1-100 pieces) | Ideal for large batches (thousands to millions of pieces) |
| Process Features | Secondary operations such as cutting, drilling, bending, and welding | Molten plastic injected into the mold for a single-shot molding process |
| Design Complexity | Limited (primarily dependent on subsequent processing) | High degree of freedom (capable of molding fine and complex features) |
| Cost per Part | Low for small batches (lower mold costs) | Very low for large batches (high mold costs amortized) |
| Surface Quality | Average (dependent on secondary operations) | Highly consistent, excellent finish (determined by mold) |
| Typical Applications | Tank liners, machine guards, custom cutting boards, signs | Bottle caps, toys, automotive parts, trash cans, and tote boxes |
Choose HDPE sheet Fabrication if:
- Large parts with relatively simple geometries: Sheet is ideal to make large, flat parts or parts with simple curves (such as tank linings, countertops, large containers, signs, and partitions).
- Flexible specifications and small batch sizes: There is no expensive tooling, so it is ideal for prototyping, one-off custom work, or small runs (typically 1-100 parts). Design or quantity changes are quick and inexpensive.
- Designs can be achieved traditionally: If your part’s final shape can be achieved by a combination of sheet cutting (sawing, laser, water jet), drilling, milling, thermal bending (folding), and welding (hot air/extrusion).
- Common applications: Linings for chemical tanks/containers, machine guards for large machinery, countertops/cutting boards for food processing, outdoor signage, water treatment tanks, generic shelving, padding, and gaskets.
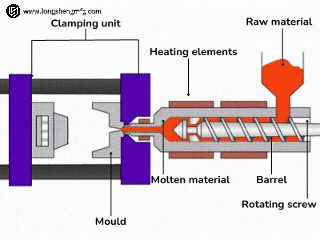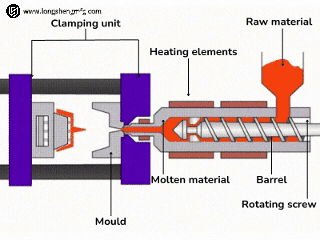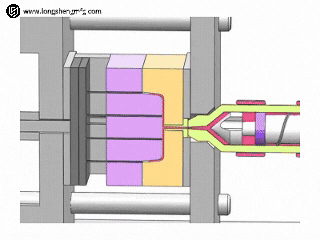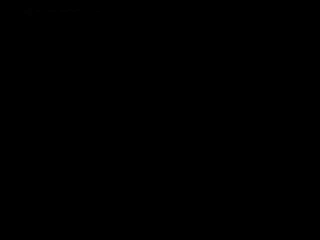
Choose HDPE injection molding if:
- Parts have complicated three-dimensional features: Injection molding is the only or most economical means of creating features with fine detail, thin walls, complex curves, internal ribs, threads, snaps, living hinges, and precisely located holes.
- Seeking high-volume production and low unit cost: Although the mold investment is high at the outset, once the mold is developed, high-volume production (in thousands to millions of parts) is extremely efficient, and the unit cost drops significantly as the volume of production rises. High automation aids in attaining high production rates.
- Require high consistency and good appearance: Injection molded parts have extremely good dimensional stability and batch-to-batch consistency. The surface finish of the mold directly impacts the finish of the product, and a variety of finishes, from matte to glossy, can be achieved to meet the demands of products with high aesthetic requirements.
- Typical applications: Various bottle closures and containers, toys, automotive interior/exterior/functional parts (fuel tanks and air ducts), housewares (trash cans, storage containers, buckets), industrial containers/transfer boxes, medical device housings/components, and snap-fit connectors.
In short: The secret to deciding between HDPE sheet fabrication and injection molding is to weigh the geometric complexity of your part against the desired volume of production. For simple geometries and small series, opt for sheet, and for complicated geometries and big series, opt for injection molding.
Is HDPE an Ecologically Sound Option?
Because plastic pollution is a global issue, the environmental sustainability of the material must be considered. Thus, high-density polyethylene (HDPE, recycling number 2) is generally a relatively environmentally friendly plastic material due to several important advantages:
Firstly, HDPE has a highly developed recycling infrastructure.
As one of the most recycled plastics, it can be “reborn” into durable new products such as municipal pipes, outdoor plastic decking, and reusable trash cans after it is cleaned, shredded, melted, and re-pelletized, effectively prolonging the lifecycle of the resource and reducing the demand for virgin plastic.
Second, HDPE items are famously durable.
From long-lasting chemical containers to weather-resistant outdoor furniture, their impact and corrosion resistance significantly prolongs their lifespan. Fewer replacements of goods mean fewer resources consumption and potential waste generation, one of the main source reduction methods.
It also has a fairly energy-efficient production process.
Its manufacture typically takes less energy and has lower carbon intensity than other common plastics like PVC or PET, offering significant environmental efficiency advantages among plastics.
Yet its limits must be clearly recognized.
HDPE remains a fossil fuel product at its origin. Its production relies on non-renewable materials (oil or natural gas), and when it is not recycled and becomes a long-lasting waste in nature, its slow decomposition process (which can take centuries) will continue to poison soil and water.
So, while HDPE is a preferable option among plastics, with recyclability, durability, and energy-conserving production, it is far from an ideal “environmentally friendly material.” The most straightforward solution to the plastic pollution issue remains to prioritize “reduce,” make every effort at “reuse,” and recycle appropriately after disposal. HDPE is merely a worthwhile stepping-stone choice along the path to a more sustainable materials economy in which it must be thoughtfully weighed. Significant environmental stewardship begins with earnest reflection and action on resource consumption patterns. There simply is no “perfect” solution to the plastics quandary.

Case Study: From Sheet Prototype to Molded Success
Customer Challenge:
A garden tool manufacturer needed to design a lightweight yet durable guard for an innovative lawn mower and wished to transition quickly from prototyping to low-cost volume manufacturing.
LS Solution:
- Rapid Prototype Verification (Sheet Metal Fabrication): The client team successfully verified 10 functional prototypes of HDPE sheet metal via CNC milling. This enabled them to finish field testing quickly, fully verifying the guard’s dimensions, overall shape, and functionality, providing a solid basis for further optimization.
- Production Design Optimization and Mold Manufacturing (Injection Molding): After prototype testing success, the client worked with LS to reduce unit cost, optimize production efficiency, and detail product features such as integrated clips and stiffeners. Our engineering team completely optimized the original design for injection molding production, ensuring manufacturability, structural integrity, and functional integrity. From this optimized design, we designed and constructed a dedicated injection mold.
Major Results:
- Dramatic Cost Reduction: Injection molding reduces the unit cost of production by 70% in comparison with sheet metal prototypes, significantly improving the competitiveness of the product in the market.
- Improving Efficiency by Leaps and Bounds: Injection molding improves production efficiency by 50 times, meeting the needs of large-scale market demand.
- Improved and Consistent Quality: The mass product far surpasses the original sheet metal prototype in aesthetic appeal, structural integrity, and overall strength, ensuring a good user experience and brand image.
This case study shows how LS, through its professional injection molding services, helps customers in seamlessly transitioning from functional prototyping to cost-effective, efficient, and quality mass production. Our core competency focus areas in mold building and design optimization directly translate to our customers in the form of significant cost savings and production efficiency, while ensuring end-product excellence.

FAQs
1. What is HDPE’s melting point?
The melting temperature of HDPE (high-density polyethylene) ranges from approximately 120°C to 180°C, depending on the molecular weight distribution and density grade of the material. The melting temperature of low-density HDPE, for example, can be around 120°C, while that of high-density grades can be 180°C. This is due to the fact that the manufacturing process and additives, such as copolymer modification, result in this difference. HDPE has good flowability in the molten state and can be easily extrusion processed or injection molded. The processing temperature must, however, be strictly controlled to avoid degradation and to realize stable material properties. Practically, one must refer to the product data sheet for the actual melting point of the respective product.
2. Is it possible to glue HDPE sheets together? ANSWER: Yes.
HDPE sheets are difficult to glue directly with ordinary glue because its low surface energy and high chemical resistance prevent the wetting and penetration of the adhesive. Successful methods include the use of special surface treatments (such as corona treatment or flame treatment) to increase surface activity, combined with commercial-grade adhesives (such as epoxy resins or cyanoacrylates). However, other techniques such as hot air welding or hot plate welding are preferred. They give stronger, more durable joints, particularly for structural or outdoor applications, and eliminate the risk of bond failure.
3. What is the difference between HDPE and UHMWPE?
The basic difference between HDPE (high-density polyethylene) and UHMWPE (ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene) is one of molecular weight and performance. UHMWPE, with a molecular weight of more than 3 million, is a “super-upgraded” HDPE version with excellent wear resistance, impact resistance, and self-lubrication much better than that of normal HDPE but difficult to process, requiring special procedures such as sintering or compression molding, and also more expensive. HDPE, on the other hand, is lower in cost and more convenient to process (e.g., injection molding), yet has inferior wear resistance. Although both are polyethylene, UHMWPE is more suitable for high-wear applications such as bearings or medical implants.

Conclusion
HDPE sheet’s excellent chemical resistance, high strength, and easy processing (cutting, hot bending, welding, CNC machining) make it an ideal choice for prototyping and low-volume production. It’s a fast and economical platform for validating designs and creating custom parts (such as laboratory countertops, corrosion-resistant tank liners, logistics boxes, outdoor signage, and food-grade countertops), providing an essential and flexible starting point for moving from concept to prototype.
Start Your HDPE Innovation Journey
Whether you need a rapid prototype, a small batch of custom parts, or evaluating large-scale production, HDPE sheet can be a crucial first step!
Upload your design or request now! Our experts will:
- Evaluate whether HDPE sheet processing is the best fit for your project (prototype/low-volume production).
- Analyze the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of large-scale injection molding and provide competitive online injection molding pricing.
Let us find the most efficient and cost-effective manufacturing path for you!
 📞 Phone: +86 185 6675 9667
📞 Phone: +86 185 6675 9667
📧 Email:info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://www.longshengmfg.com/






Loving the info on this site, you have done great job on the blog posts.