For the manufacturing industry, where one has to do prototype making or mass producing, a majority of decision-makers find themselves stuck in a dilemma: die casting or injection molding? While both technologies have a similar shape, they differ in type. Metal-oriented die casting is best suited for parts with high strength, heat resistance, and intricate geometries, such as car engines or precision gears. Injection molding, on the other hand, is a plastics expert and is best suited to rapidly mass-produce lightweight, insulating, and irregularly shaped goods such as housings, consumer products, or connectors. The key to choosing a process is not to aim for unadulterated dominance over some other, but to choose the right one based on product functionality, material properties, cost margin, and production size—there is no “best” but “most appropriate.” Realizing this underlying difference is the key to effective manufacturing. To save your time, below are the highlights in brief.
Die Casting vs. Injection Molding Core Comparison Table
| Characteristic Dimensions | Die Casting | Injection Molding |
| Material Type | Metal (e.g., aluminum, zinc alloy) | Plastic (e.g., ABS, PP, nylon)
|
| Product Cost | Mold investment is extremely high, but unit cost decreases significantly with increasing production volume. | High mold investment, extremely low unit cost
|
| Production Speed | Short cycle time, suitable for large-scale production. | Extremely short cycle time (seconds), extremely high efficiency |
| Part Strength | High strength, high hardness, high temperature resistance | Lower strength, lightweight, insulating |
| Applicable Applications | Structural parts, load-bearing parts, high-temperature/corrosion-resistant parts (e.g., engine housings, gears) | Appearance parts, housings, lightweight insulating parts, consumer goods |
- Choose Die Casting: When you need to make high-strength, wear-resistant, and heat-resistant metal parts.
- Choose Injection Molding: When you need to make lightweight, insulating, or high-tech-looking plastic parts cheaply and quickly in large quantities.
The determining factor is always the end use and required material properties (metal or plastic) and not the inherent qualifications of the process.
Why Trust This Guide? Real World Experience from LS Experts
At LS Precision Manufacturing, we’ve been deeply engaged in precision manufacturing for nearly two decades. Our daily focus is finding the optimal solution for our customers in two key processes: die-casting and injection molding. Not only do we possess advanced equipment, we also possess a deep knowledge base of materials science, mold design, and production optimization. It’s not a hypothetical suggestion; it’s the essence of hundreds of thousands of experiments, pilot production, and large-scale manufacturing expertise. It is meant to help you cut through the white noise and get down to the nub of your decision-making.
A case is cited from our automotive components business. A customer urgently required a sensor bracket for an engine casing which required high strength at low and high temperature with great weight saving. We rapidly assembled a team, and from our excellent understanding of material properties, we ruled out the first proposed high-strength engineering plastic solution and ultimately arrived at aluminum alloy die-casting. Through the precision of mold design and vacuum die-casting technology, we successfully obtained a part which not only weighed 30% less, but also far more than the customer could hope for in terms of high-temperature strength and structural performance. It exists to this day as a good sound in millions of vehicles. This is the power of giving you hands-on experience.
What Is Die Casting? What Is Injection Molding? What Are The Main Differences?
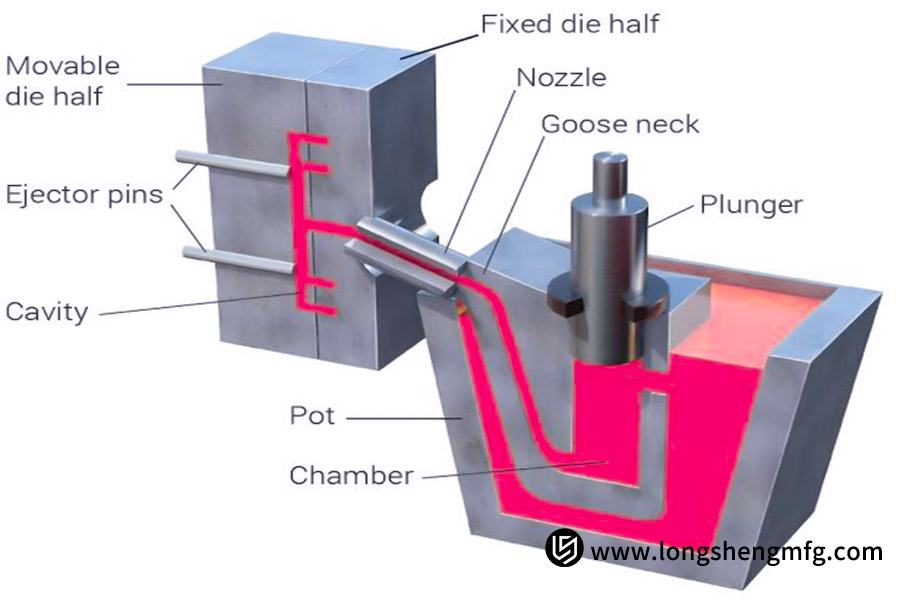
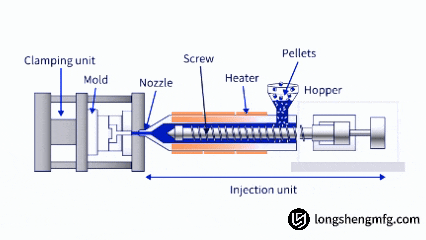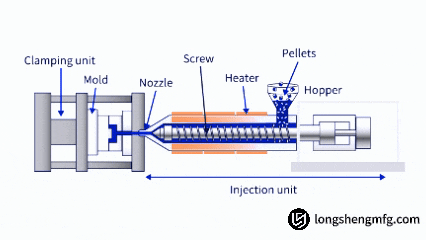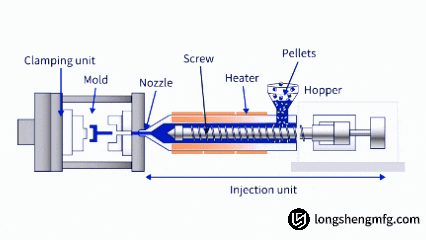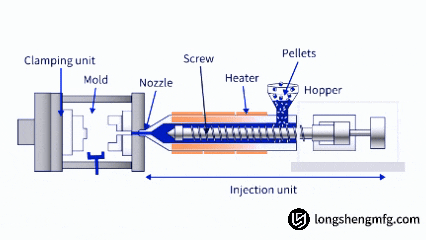
Die casting is the process whereby liquid metal (such as an aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, or magnesium alloy) is pushed at high speed and high pressure into a metal mold cavity of precise dimensions. The metal part is subsequently cooled and formed. Die casting has less cycle time and can be applied in large production. Its underlying philosophy is to embrace the use of high pressure to force exact liquid metal into the mold in order to form parts of intricate geometry, exact dimensions, and fine mechanical properties.
Injection molding, however, is an injection molding technology for thermoplastic or thermosetting plastic. Plastic pellets are melted and warmed, and they are later injected under low pressure into the mold cavity. The plastic item is subsequently hardened when cooled. It is an extremely effective process and suitable for manufacturing lightweight, insulating, and diversely shaped items such as containers, housings, and consumer goods. The essential distinctions between the two are based on the three categories of material, molds, and equipment.
| Comparative Dimensions | Die Casting | Injection Molding |
| Material Type | Metal (aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, etc.) | Plastic (ABS, PP, nylon, etc.)
|
| Mold Requirements | Steel material, extremely high strength, resistant to high temperatures and high pressures. | Mostly mold steel, with lower pressure tolerances.
|
| Equipment Features | Die casting machines have high clamping force, and the injection system is resistant to metal corrosion. | Injection molding machines are relatively lightweight and focus on uniform plasticization. |
- Fundamentally, the most significant difference between injection moulding and die casting is material properties: one is metal, the other plastic.
- This has an immediate translation into fundamental differences in equipment capability, mould design, and end-product performance. It is realizing this, and not more complex points, that will enable you to choose the right process route.
What Are The Specific Advantages Of Die Casting? When Do You Choose Die Casting?
As a pioneering metal forming technology, die casting has numerous uncommon advantages impossible to substitute and hence a critical technology in the manufacturing of high-volume metal parts.
These advantages are largely reflected on four fronts:
- Superior strength and toughness. Molten metal is filled into the mold cavity under pressure conditions and consolidated into a dense, non-porous microstructure. This offers parts with excellent mechanical properties, high impact strength, and better high-temperature integrity, much better than most traditional castings and plastics.
- Very high dimensional accuracy. Techniques like aluminum die casting can create parts having very complicated configurations, thin-walled parts, and better dimensional stability, reducing the machining effort and decreasing costs for future assembly by much.
- Better surface finish. Die castings offer a clean and delicate surface, and second processing can be carried out directly on them such as electroplating and painting to conveniently achieve a high-quality finish.
- High productivity. After preparation of the mold, die casting is able to produce dozens of molds every minute, making it highly appropriate for large quantity orders in sectors such as aerospace and automotive.
Thus, when would you employ die casting? Die casting will be most appropriate for your project if the following conditions are met:
- Material Requirements: The part should be fabricated out of metal, especially when aluminum die-casting or other light alloys are needed to create a light weight with high strength.
- High Volume: Hundreds of thousands or millions of units have to be produced to distribute the cost of the high tooling.
- Performance Specifications: The component must be capable of withstanding hostile environments, high temperatures, or high structural loads and be highly reliable.
- Sophisticated Design: The component geometry is advanced and requires strict dimensional accuracy and consistency.
In high-volume, high-performance production of sophisticated metal structures, high-pressure die casting is unquestionably the best option with economy and excellent performance.
When Is Injection Molding A Better Option?
When your product design is plastic-based and requires high cost-effectiveness, speed of production, and visual precision, injection molding is certainly a better choice than die casting.
Making plastic parts with extremely intricate shapes
Injection molding offers unparalleled advantages in making plastic parts with extremely intricate shapes. It is able to make complex three-dimensional geometries with snap-fits, living hinges, fine textures, and thin walls in a single step. They are common in enclosures of electronic equipment, appliance parts, and consumer goods. This near-infinite design freedom allows product designers to achieve high levels of integration as well as aesthetic innovation.
Economy-of-scale mass production at low prices
Injection molding has excellent cost benefits in economy-of-scale mass production at low prices. While molds are costly, after the creation of the mold, the part cost is amortized to a very low level. Its very high rates of production (cycle times are usually seconds) enable it to produce orders of hundreds of thousands or even millions of parts with phenomenal effectiveness, a capability not matched by most metal processing methods.
Rapid prototyping and small-batch test production
Injection molding is appropriate for rapid prototyping as well as small-batch test production. With the help of elastic molds (e.g., aluminum molds) and 3D printing technology, companies can produce functional prototypes to test at a low price within a very short cycle, significantly shortening product development cycles and time to market.
Typical applications are:
- Consumer electronics: mobile phone cases, laptop docks, headphone pods.
- Medical devices: syringes, IV tube connectors, sterile packaging.
- Automotive interiors: buttons, trim, vent grilles.
- Consumer goods: toys, bottle caps, kitchen utensils.
If you need to produce complex cost-conscious plastic components that don’t require the characteristics of metals, injection molding is your first choice.
Cost Comparison: Die Casting vs. Injection Molding: Which Is More Economical?
Is injection molding or die casting more cost-effective? It is impossible to know for sure. Economic efficiency is highly subject to the level of production, material selection, and component design. A truly economical option requires a thorough balancing act of many variables, such as mold investment, unit cost, and material costs. The following table merely shows a contrast between the two using a cost structure approach:
| Cost Dimension | Die Casting | Injection Molding | Analysis Description |
| Mold Investment | Very High | High | Die casting molds must withstand high-temperature and high-pressure molten metal, requiring the use of top-quality mold steel and precision machining. Costs are typically twice as high as those of injection molds or even higher. |
| Unit Cost | Medium to Low | Very Low | Die casting has a higher unit material (metal) cost, but high production efficiency in large volumes allows for efficient mold cost amortization. Injection molding, especially for plastics, has an extremely low unit cost, offering significant advantages in ultra-large-scale production. |
| Material Cost | High | Low | Metal alloys (such as aluminum) are generally much more expensive than engineering plastics (such as ABS and PP). |
| Post-Processing Cost | High | Low | Die-cast parts often require secondary processing such as deburring, drilling, tapping, and surface treatment (such as sandblasting and electroplating). Injection-molded parts can often be formed in a single step and assembled directly, requiring minimal post-processing. |
- When die casting is cheaper: Your item requires metal to meet up with strength, temperature-resistant, or conducting needs, and your annual manufacturing quantity is big enough (typically tens of thousands or more), large enough to make up for the expense of high mold and material costs.
- When injection molding is cost-effective: Your product is plastic and requires a very low unit cost to be viable for high-volume production runs involving hundreds of thousands or even millions of units. Injection molding (especially if with basic molds such as aluminum molds) also offers greater cost latitude for small and medium production volumes or prototyping.
- No outright more cost-effective process; only the process best suited for the project requirements.
- Die casting is more cost-effective if the component must be metal and high volume; injection molding is surely more cost-effective if the component is plastic and in very high volume.
- The final decision must be carefully worked out based on some production goals and material performance requirements.
Material Selection Guide: Metal Or Plastic?
Material selection is essential in product development, and it has a direct impact on product performance, cost, quality, and the user experience. The two most used materials are metal and plastic, both with different characteristics. In order to make the correct choice, an understanding of their difference is necessary.
Metal
Metal alloys (such as zinc and aluminum alloys) have excellent mechanical properties, with high strength, hardness, and stiffness with impact and wear resistance and thus can be utilized in making structural parts in high-impact or load applications. Moreover, metals have good heat insulation and thermal or electrical conductivity and can withstand high-temperature conditions (such as engine peripherals) and meet electromagnetic shielding needs. Metallic items possess a heavy mass sensation, and methods such as anodizing and electroplating can achieve a high-grade metallic look and feel.
Plastic
Plastic items (such as ABS, PC, The advantages of Nylon are its light weight, good insulation, and styling versatility. Plastic parts are readily producible into very complex shapes and can achieve a huge range of colors and surface finishes (such as glossy, flat, and metallic surfaces). While their overall strength and thermal resistance tend to be lower than for metals, most engineering plastics are within the requirements of most consumer products and home appliances. Plastics are cost-effective, especially for mass production.
Selection Guidelines:
- Use metal when your product requires: high strength, high thermal resistance, high heat/electrical conductivity, load-supporting structural components, or a high-end metallic look. Typical applications include car parts, machine enclosures, top-quality hardware, and heat sinks.
- Use plastic whenever your application requires: thin materials, complex shapes, wide range of color and finish, insulation, low cost, and mass output. Examples include electronic equipment enclosures, consumer products, packaging, and medical equipment.

Relative Cost Of Production Cycle: Which Process Offers Faster Delivery?
In product manufacturing, production cycle has a direct effect on project advancement and market adaptability. Delivery rates for die casting and injection molding are quite disparate, varying mainly in three important phases.
1. Mold manufacturing:
The initial step is mold manufacturing. Injection molds are able to employ streamlined processes, i.e., aluminum molds, shortening prototype mold manufacturing cycles to 1-2 weeks, significantly speeding up sample checking. Die cast molds have to be constructed from high-temperature and pressure-resistant mold steel, which requires very high precision machining. The manufacturing cycles are 8-12 weeks, requiring high initial investments.
2. Mass production:
Both methods are of high productivity as soon as mass production is initiated. Injection molding offers a massive head start in cycle time, typically between 15 and 60 seconds per item, and enables uninterrupted, rapid production. Die casting also takes a longer cycle time of approximately 30 seconds to 3 minutes, but also offers efficiency in output with its high-pressure injection.
3. Post-processing processing:
Post-processing processing is also significant. Die castings often require secondary procedures such as degating, polishing, and electroplating, which accounts for additional time and cost. Injection molded parts generally have more integration and possess relatively uncomplicated post-processing requirements, which saves overall delivery time.
- If rapid first-time delivery is desired, especially for plastic parts, injection molding is advantageous due to its shorter mold cycles and productive operation.
- For long-run applications with the use of metal materials, while longer lead times might be required for die casting, its steady mass production ensures constant efficiency in delivery.
LS Case Study: How To Select The Optimal Production Process For An Automotive Parts Customer?
1. Client Challenge:
A large automotive component supplier was required to produce a sensor bracket for an engine. The part needed to have reliable operation in the temperature range -40°C to 150°C, be of very high structural stiffness to resist engine vibration, and be at least 30% lighter than the base steel component. Production was annually about 100,000 units, and prices needed to be in target brackets.
2. Limitations of Traditional Solutions:
The customer initially considered two traditional solutions: engineering plastic injection molding or traditional steel stampings. Injection-molded parts, however, lacked the high-temperature characteristics and strength required in extreme environments. While the steel parts supplied the necessary strength, they were too heavy and cumbersome to form into complicated structures. Traditional die-casting shops would typically just recommend die-casting with aluminum alloys, but an all-metal solution could lead to cost overruns.
3. LS Precision’s Creative Solution:
LS Precision hired consultants and asked them to conduct a detailed analysis from three perspectives: materials, processes, and economics. Rather than simply choosing either one or the other, we provided an innovative hybrid material solution: the load-carrying structure was fabricated with high-strength aluminum alloy die-casting reduced in weight by optimized rib design and wall thickness distribution. Insulating connections were injection-molded with high-temperature-resistant special engineering plastics. As an experienced die-casting plant, we developed a new mold design to enable a smooth integration of metal and plastic components.
4. End Results and Value:
The innovative solution successfully incorporated a part that was 35% lighter than the respective steel part, fully complied with temperature resistance tests, and performed incredibly well in vibration testing. By streamlining the process, the overall cost was reduced by 22% compared to the all-metal solution, thus achieving the company’s yearly goal of production at 100,000 units. The customer not only got a flawless product but also established a long-term strategic partnership with LS Precision with this project, which enables them to jointly establish even more sophisticated automotive lightweighting projects.

How To Choose The Most Appropriate Process Based On Product Demands?
Process selection in the manufacturing industry has a direct impact on the quality of the product, its price, and productivity of manufacture. Faced with the two entrenched processes of injection molding and die-casting, most decision-makers find themselves in a dilemma. Practically, the correct selection does not rely on the strengths of the process but rather on a programmed and precise matching of the needs of the product to process characteristics.
1. Material requirements
Material requirements play the largest role in determining the choice of process:
- If metal characteristics (such as better strength, high-temperature resistance, and electrical conductivity) are needed by the product, die-casting is the better option.
- If the product needs to be lightweighted, insulated, or to have a broad range of appearances, injection molding will be the best option.
2. Economies of scale
Economies of scale is a key economic measure of viability. Injection molding renders enormous advantage in the cost of molds as well as cycle of production in the scenario of low-volume production. However, one can gain the advantage of die-casting scale only if one produces tens of thousands or tens of thousands of units.
3. Comprehensive consideration
The product structural intricacy, dimensional accuracy demands, and post-processing requirements should be considered. Metal parts of complex structure, thin walls, and high precision requirements are most suited for die casting, while injection molding is optimal when complex surface treatment and integrated molding are involved.
- Process selection is a decisive decision-making process by product characteristics, production rate, and material characteristics. Based on rational analysis of these decisive factors, firms are able to find out which solution is most suitable for production.
- Preparing samples for inspection and, if necessary, consulting an expert manufacturer (LS Precision) is recommended so that the chosen process route is able to satisfy the product requirement and be cost-effective.
FAQs
1. Can die-cast parts be processed after injection molding?
Yes. Die-casting parts can be widely used as inserts and molded into plastics through the insert molding technique to obtain a combined metal-plastic mold. The process utilizes the strength of metals as structural components and plastic as insulating and lightweight material. The process is widely used in automobile components, electronic hardware components, and other products, significantly improving the functional integration and aesthetic appearance of the product.
2. Is die-casting suitable for small-batch production?
Not likely. Die-casting has high initial investment in mold, and recovering the cost in small-volume production is not possible. For low-volume production needs, other methods such as CNC machining, 3D printing, or simple mold injection molding are recommended. LS Precision can provide the most cost-effective customized solutions based on your volume of production, material, and accuracy requirement.
3. Can the strength of injection-molded parts reach the same level as metal?
By incorporating reinforcements such as carbon fiber and glass fiber, and by employing design optimisations such as ribs and structure integration, mechanical performance of engineering plastics can be enhanced significantly to levels of some aluminum or zinc alloys. However, since plastics are inherently different from metals, especially in aspects such as rigidity, heat resistance, and fatigue resistance, certain special conditions of application must be complied with.
4. How can I obtain professional process selection advice?
LS Precision offers free technical consulting services. Seasoned engineers conduct a serious analysis based on your product requirements (e.g., material characteristics, production volume, cost, and cycle time) to offer you the most appropriate manufacturing process and material recommendation. LS Precision Manufacturing also help prepare samples, which allow you to make good decisions and prevent development risks.

Conclusion
Die casting and injection molding are two preferred production methods with a myriad of application possibilities. Die casting has high strength, precision, and endurance in large-scale manufacture of metal parts and is hence a backbone of premium manufacturing industries such as auto and aircraft. Injection molding, on the other hand, has unparalleled productivity and versatility and is hence the preferred method in large-scale production of plastic household appliances, electronics, and medicines. The core idea to choosing a process is in careful examination of the product material requirement, production amount, cost tolerance, and performance requirement. There is no sub-perfection or perfection but best fit.
If you are still struggling to choose processes, LS’s skilled professionals are here to assist you. Our process experts will provide you with scientific process assessments, material recommendations, and custom manufacturing solutions based on your product requirements. Contact LS Precision and let us use our experience in assisting you to reduce development risk, reduce production costs, and work together to develop the best competitive products.
 📞 Phone: +86 185 6675 9667
📞 Phone: +86 185 6675 9667
📧 Email:info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://www.longshengmfg.com/
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. LS makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through LS’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please contact to our for more information.
Team LS
This article was written by various LS contributors. LS is a leading resource on manufacturing with CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, injection molding,metal stamping and more.






You can certainly see your skills within the paintings you write. The sector hopes for more passionate writers such as you who are not afraid to mention how they believe. Always follow your heart.
It is the best time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I desire to suggest you few interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read even more things about it!
Thank you very much for your suggestions and encouragement! You’re right, this is indeed a great time to start planning. The topics you mentioned are very interesting, and I’ve made a note of them. I will definitely consider them carefully when planning future content. Please feel free to share any more ideas with us!
Thank you so much for your profound and poetic words. Your words have been a great inspiration to me. I hope you will always follow your heart!
I have been exploring for a bit for any high quality articles or weblog posts on this kind of space . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this site. Studying this information So i am satisfied to convey that I’ve a very just right uncanny feeling I came upon exactly what I needed. I most without a doubt will make sure to do not forget this site and provides it a glance on a continuing basis.
I’d always want to be update on new blog posts on this site, saved to bookmarks! .
I just could not depart your website prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard info a person provide for your visitors? Is gonna be back often to check up on new posts
Well I sincerely enjoyed reading it. This article provided by you is very helpful for good planning.