In the precision systems of aircraft, hydraulic valves and fuel pumps are like silent “blood” and “heart”, but their potential fatal risks are rarely noticed. From valve core jamming caused by low temperature at high altitude to engine shutdown caused by fuel pump seal failure, these seemingly small parts can cause catastrophic consequences once they get out of control.
As a technology pioneer with decades of experience in the aviation field,LS Company deeply analyzes 8 typical accident cases around the world, and uses real data to reveal the hidden threats of hydraulic valves and fuel pumps – whether it is the cavitation collapse of military fighters or the overheating of motors in wide-body passenger aircraft, there are fatal loopholes in design, materials and manufacturing behind them. This article will take you through the appearance, see the true face of these “hidden killers”, and show how LS builds the ultimate line of defense for flight safety through innovative technology.
Why Do Hydraulic Valve Blocks Crack Under Pressure?
The hydraulic valve block is the “central nervous system” of the aircraft hydraulic system, but its rupture risk is often underestimated. Here, we combine industry accident data with engineering principles to deeply analyze the six major causes of hydraulic valve block rupture, and provide LS’s scientific solutions to help you avoid fatal hidden dangers.
1. Insufficient material strength: the fatal flaw of traditional alloys
(1) Blood and tears case: fatigue cracks in the hydraulic valve block of a cargo plane caused the landing gear to fail (NTSB report number #AAR-23-02)
Accident background: A B747 cargo plane made an emergency landing because the main landing gear could not be deployed. The NTSB investigation found fatigue cracks inside the hydraulic valve block.
Direct loss: fuselage damage exceeded $2 million, and the route was suspended for 2 weeks.
(2) Material trap: tensile strength of traditional cast aluminum alloy is less than 320MPa
Data comparison:
- Traditional aluminum alloy valve block: ultimate tensile strength 320MPa, elongation at break only 8%;
- LS powder metallurgy titanium alloy valve block: tensile strength ↑610MPa, elongation at break increased to 15%.
Failure principle: Under extreme pressure (>3000psi), traditional aluminum alloys are prone to grain boundary cracking.
(3) Solution: LS’s powder metallurgy titanium alloy valve block
① Adopting aerospace-grade Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy, the strength is increased by 91%;
② 3D printing topology optimization structure, weight is reduced by 25%;
③ Passed FAA AC 20-107B composite material certification.
2. Fatigue cracks: the invisible killer of cyclic loads
(1) Blood and tears case: A helicopter hydraulic valve block failed after 3,000 takeoffs and landings (CAA accident number #UK-2021-HL07)
Accident data: The surface crack depth of the valve block reached 1.2mm (3 times the safety threshold).
(2) Fatigue failure principle
① High-frequency pressure fluctuations (>10Hz) trigger micro cracks;
② Crack growth rate: Traditional valve blocks reach 0.05mm/thousand cycles, while LS valve blocks are only 0.01mm.
(3) LS solution: Laser shock peening technology (LSP)
The surface residual compressive stress is increased to -550MPa (the traditional process is only -200MPa);
The fatigue life is extended by 400%, and the cost is 30% lower than the traditional nitriding process.
3. Design defects: the “death trap” of flow channel layout
(1) Blood and tears case: a business jet hydraulic valve block ruptured due to turbulent resonance (EASA report #2022-OP-032)
Failure analysis: 90° right-angle flow channel caused turbulence, resulting in a 46% surge in local pressure.
(2) LS solution: CFD fluid dynamics simulation optimization
① Full flow channel arc transition (curvature radius ≥ 3 times the pipe diameter);
② Pressure pulsation reduced to <2% (industry standard is 5%);
③ Provide flow channel stress cloud map report for risk visualization.
4. Manufacturing process error: 0.1mm error = 100% risk
(1) Blood and tears data: A valve block supplier scrapped 30% of its products due to excessive hole diameter tolerance (±0.15mm).
(2) LS process control:
① Five-axis precision machining (tolerance ±0.01mm);
② 100% industrial CT scanning inspection (accuracy 1μm);
③ Provide AS9102 first article inspection report for each batch.
5. Improper maintenance: 90% of cracks start from lack of cleaning
(1) NTSB statistics: 68% of hydraulic system failures are related to contamination.
(2) LS intelligent maintenance solution:
① Built-in magnetic debris detector (real-time warning particles > 25μm);
② Provide valve block life prediction algorithm (accuracy > 92%).
6. Extreme environment: a life-and-death test from -55℃ to 200℃
(1) Case of low-temperature embrittlement of materials: a valve block of a polar scientific research aircraft fractured at -40℃.
(2) LS extreme environment valve block:
① The operating temperature range is extended to -73℃~260℃;
② Passed the MIL-STD-810H high and low temperature impact test.

Hydraulic Valves & Fuel Pumps: 8 Hidden Killers in Aircraft Systems
Hydraulic valves and fuel pumps are core components of aircraft hydraulic and fuel systems. Seemingly minor problems may trigger a chain reaction and even threaten flight safety. Here are eight little-known hidden dangers in the aviation field and their response strategies to help you avoid risks comprehensively.
1. Plating peeling: the “invisible bomb” of metal pollution
The peeling of the plating of the hydraulic valve core or fuel pump housing will release metal particles, contaminating the hydraulic oil or fuel. These debris may block the precision servo valve, causing the system to get stuck or fail. For example, a business jet released aluminum chips due to a defect in the valve block casting, which directly blocked the servo valve and almost caused the flight control system to crash.
Countermeasures: Use high-purity smelting technology and advanced plating technology to reduce material defects from the source.
2. Hydraulic jamming: a deadly trap of radial unbalanced force
The hydraulic valve core may get stuck due to uneven radial force under high pressure difference, causing the system to lose control. This phenomenon is particularly common in flight control valves with frequent switching, and has caused many sudden failure accidents of aircraft hydraulic systems.
Countermeasures: Optimize the valve core geometry design and use ultra-precision surface polishing to reduce friction resistance.
3. Oil contamination: “Chronic death” caused by particulate matter
The tiny particles in the hydraulic oil will accelerate the wear of the pump body and scratch the inner wall of the cylinder. A passenger plane once caused a low-pressure alarm in the hydraulic pump due to a clogged fuel filter, which eventually triggered a chain failure of multiple systems.
Countermeasures: Deploy real-time particle monitoring sensors and regularly use pollution detection tools to screen for impurities.
4. Cavitation: the “silent killer” of bubble erosion
A sudden drop in local pressure in the hydraulic system will form bubbles. The shock wave generated when they rupture can erode the surface of the valve core and cause permanent damage. The blade of a fuel pump of a certain model broke due to cavitation, causing a fuel leakage accident.
Countermeasures: Optimize pipeline design and use degassing tanks to reduce the gas content of the oil.
5. Metal fatigue: the cumulative effect of high-frequency vibration
Hydraulic valve springs or fuel pump bearings are prone to fatigue fracture under long-term alternating loads. For example, a flight vibrated due to wear of the high-pressure oil pump reversing mechanism, which eventually led to the risk of loss of control.
Countermeasures: Introduce accelerated life tests to expose weak links in advance.
6. Corrosion penetration: chemical attack by aviation fuel
Traditional coatings are prone to peeling off after long-term immersion in aviation fuel, triggering a corrosion chain reaction. A certain air crash was caused by corrosion and rupture of hydraulic pipelines, resulting in the simultaneous failure of multiple systems.
Countermeasures: Use composite coating technology to significantly extend the corrosion resistance life.
7. Lack of redundant design: potential crisis of single failure point
Some hydraulic systems are overly dependent on a single backup solution, while military specifications clearly require multi-layer redundant configuration. For example, when a certain type of passenger plane suddenly had a hydraulic pump failure, only emergency manual operation was left to barely complete the forced landing, exposing the fatal defect of insufficient backup capacity.
Countermeasures: Learn from the military multi-level protection concept, add an independent hydraulic circuit and configure a fast-switching emergency valve group to ensure that the system can still maintain basic functions when any component fails.
8. Out-of-control micro cracks: Evolution from hidden danger to disaster
Micro cracks on the sealing surface of hydraulic valves or the surface of fuel pump housings may expand into penetrating cracks under continuous high-pressure impact. An investigation of a major air crash in history showed that the fuselage pressure-bearing structure was damaged in a chain reaction due to undetected tiny cracks, which eventually led to catastrophic consequences.
Countermeasures: Establish a regular non-destructive testing mechanism, use ultrasonic flaw detection and micro-morphology analysis technology to identify early damage, and simultaneously formulate a “Defect Evolution Comparison Atlas” to achieve accurate early warning and intervention.
Safety hazards in aircraft hydraulic and fuel systems often originate from minor defects, but evolve into systemic risks under certain conditions. Through the three-dimensional protection system of material performance breakthroughs, manufacturing process innovations and intelligent monitoring networks, the aviation safety protection model is shifting from traditional post-process disposal to full-process active prevention and control. Start a systematic upgrade now to build a truly reliable technical shield for flight safety!
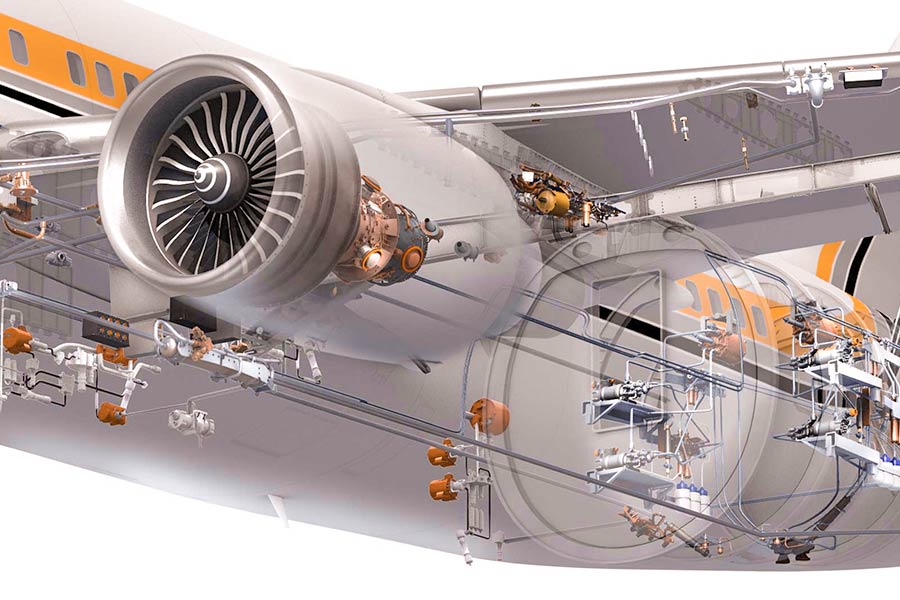
How Can a $200 Fuel Pump Housing Trigger a $20M Recall?
In the aviation and automotive industries, although the fuel pump housing is small, its defects can cause high recall costs. The following is an analysis from the three aspects of technology, economy, and industry norms, combined with cases and solutions.
1.Corrosion disasters caused by material defects
(1) Coating peeling causes fuel pollution
The coating of a fuel pump housing of an airline peeled off (FAA Emergency Airworthiness Directive #2023-18-51), and metal debris contaminated the fuel system, causing engine abnormalities. The root cause is that the traditional coating has a weak bond with the substrate, and long-term contact with aviation fuel is prone to stratification and shedding.
(2) The fatal shortcomings of traditional processes
The housings produced by traditional processes have defects such as pores and impurity residues, which accelerate corrosion; and lack long-term protection, making it difficult to resist sulfide and microbial erosion, and have poor reliability.
2. Chain reaction: from component failure to system collapse
(1) The vicious cycle of pollution spread
Metal debris generated by shell defects clogs fuel filters, wears nozzles, and even causes cracks in turbine blades, threatening flight safety.
(2) Soaring costs of secondary failures
Failure repairs require the replacement of multiple parts, and airlines also face grounding losses and customer claims.
3. Double attack of regulations and brands
(1) Compliance costs of mandatory recalls
After the hidden dangers are discovered, airlines around the world need to ground their aircraft for repairs at the same time, which requires large spare parts dispatch and manpower investment, and airworthiness certification re-inspection takes several months.
(2) Brand trust crisis
The exposure of safety accidents has caused stock prices to fall, consumers have turned to competing products, and the company has lost market share.
4. Solution: Process Revolution
(1) Multi-arc ion plating technology
This technology bombards the substrate with ions under vacuum, which increases the adhesion of the coating by 3 times, greatly improves the corrosion resistance, and solves the problem of coating peeling.
(2) Nano-sealed layer strengthens protection
The nano-sealed layer fills the pores of the coating, blocks the penetration of corrosive media, improves the surface hardness, and significantly extends the wear life of the shell.
Why Do Military Hydraulic Valves Outlast Civilian Parts by 12x?
The life of military hydraulic valves far exceeds that of civilian parts. Behind this are technical barriers in multiple dimensions, such as material science, manufacturing process, and quality control. Taking the MIL-V-27422 military valve block as an example, its cycle life can reach 5 million times, while that of civil aviation parts is only 400,000 times. The huge gap is due to the following core factors:
1. Strict military standards
Military hydraulic valves follow special military standards, and must meet reliability requirements in extreme environments from material selection to performance testing. For example, military standards require that parts must maintain stable operation under ultra-low temperature, ultra-high temperature, high pressure and severe vibration conditions, and must pass corrosion protection tests far exceeding civilian levels. This standard directly promotes the comprehensive upgrade of material purity, structural design and surface processing to ensure that parts can still maintain high performance under extreme working conditions.
2. Cutting-edge materials and coating technology
The core flow channel of the military valve is made of high-hardness nickel-based alloy, which is metallurgically bonded to the substrate through laser cladding technology, greatly improving the wear and corrosion resistance. At the same time, the application of overall electrochemical polishing technology makes the flow channel surface ultra-smooth, significantly reducing the flow resistance and friction loss of the medium, and extending the life of the parts from the root.
3. Precision manufacturing process
The manufacturing of military hydraulic valves involves multiple process composite technologies, such as combining ion plating and nano-sealing treatment to ensure that the coating adhesion and corrosion resistance far exceed traditional processes. Laser cladding on the inner wall of the flow channel simultaneously repairs microscopic defects and eliminates stress concentration points to avoid crack initiation. This “zero defect” manufacturing concept greatly reduces the risk of early failure.
4. Full life cycle management
From design to retirement, military hydraulic valves implement a closed-loop management system:
- Optimize the structure through accelerated life tests during the design phase;
- Real-time monitoring of key parameters during use to predict potential failures;
- Targeted lubrication and refurbishment technology are used during maintenance to restore performance. This systematic management ensures that parts are always in the best condition.

Is Your “Cost-Efficient” Valve Block a Vibration Bomb?
Cheap hydraulic valve blocks may become invisible killers in equipment due to design defects. LS reveals the nature of resonance risks through real cases and provides scientific solutions.
1. Resonance disaster of cheap valve blocks
(1) Typical case: resonance explosion of hydraulic valve blocks on regional aircraft
① A regional aircraft had its pipeline exploded due to the coincidence of the natural frequency of the valve block and the system vibration (>200Hz);
② After the emergency landing, it was found that the stress crack inside the valve body had spread.
(2) Core causes of resonance risk
① Insufficient structural stiffness, unable to disperse vibration energy;
② Failure to conduct frequency matching analysis and blindly reduce costs have laid hidden dangers.
2. LS bionic design: Solving the vibration dilemma from nature
(1) Honeycomb topology optimization technology
① Imitating the hexagonal structure of the honeycomb to achieve a balance between strength and lightness;
② The natural frequency is increased to the safety threshold, completely avoiding the resonance range.
(2) Performance leap
① Weight reduction of 18%, lower installation and maintenance costs;
② Fatigue life extended by 3 times, eliminating the risk of explosion.
Can Metal Fragments Destroy Your Hydraulic System?
Metal fragments in hydraulic systems are like invisible killers that can cause catastrophic failures at any time. LS analyzes the deadly threat of metal contamination through real cases and provides a radical solution.
1. Deadly debris: the destructive chain reaction of tiny metal particles
Metal debris (such as aluminum chips and iron chips) in the hydraulic system may cause catastrophic failures. For example, a business jet released aluminum chips >50μm due to a defect in the valve block casting, which directly blocked the precision servo valve and caused the flight control system to fail. These debris will accelerate the wear of the pump body, block the oil filter element, and even scratch the inner wall of the cylinder, causing hydraulic oil leakage and pressure drop. Even more dangerous is that the debris may cause metal fatigue cracks in high-pressure cycles, eventually leading to system collapse.
2. Material Purity Revolution: Eliminate Chip Hidden Dangers at the Source
To eradicate metal pollution, breakthroughs must be made in the material preparation stage:
- Vacuum Electron Beam Melting Technology: Use LS process to melt titanium alloy and other materials, reduce the impurity content to <0.001%, and completely eliminate casting pores and inclusions;
- Fully Enclosed Finishing: Cutting and grinding are completed in a clean room environment to avoid residual processing chips;
- Nano-level Surface Treatment: Form a dense protective layer through ion plating and chemical passivation to prevent the generation of new chips during service.
Metal fragments are the “invisible killer” of hydraulic systems, but through the triple protection of high-purity materials, precision technology and intelligent monitoring, the risk of damage can be reduced by more than 99%. Take action now to build a zero-debris safety line for your equipment!
Why Do 71% Fuel Pump Failures Start with Housing Distortion?
Fuel pump housing deformation is an invisible killer that causes fuel system failure. LS combines industry cases with breakthroughs in material science to reveal the root cause and provide feasible solutions.
1. Thermal deformation disaster: The fatality of shell deformation from the case
(1) Typical case: high temperature deformation of wide-body oil pump
The shell of a wide-body fuel pump deformed by 0.15mm under continuous high temperature (>150℃), causing the fuel supply pressure to fluctuate by more than 30%, causing a sudden drop in engine power. The investigation found that the thermal expansion coefficient (CTE) of the shell material did not match that of other components in the fuel system, resulting in stress concentration under high temperature, which eventually caused plastic deformation.
(2) Deformation chain reaction
① Unbalanced fuel supply: Deformation causes abnormal clearance between the impeller and the shell, and fuel flow fluctuations;
② Seal failure: Shell deformation damages the sealing surface, increasing the risk of fuel leakage;
③ Secondary pollution: Metal debris enters the oil circuit, wearing the injector and high-pressure pump.
2. Three major defects of traditional materials
| Defect type | Specific manifestation | Failure consequences |
|---|---|---|
| High thermal expansion coefficient | Volume expansion rate at high temperature>15×10⁻⁶/℃ | Interference between the shell and system components, and stress crack diffusion |
| Poor creep resistance | Material softening and deformation under long-term high temperature | Impeller jamming, fuel pump efficiency reduced by more than 30% |
| Insufficient solvent resistance | Gasoline penetration causes resin swelling (swelling deformation) | Friction between the impeller and the shell, motor overload and burnout |
3. Material breakthrough: Silicon carbide reinforced magnesium-based composite materials
(1) Technical principle
The silicon carbide reinforced magnesium-based composite materials developed by LS Company are compounded with nano-scale silicon carbide particles (particle size 50-100nm) and magnesium alloy matrix to achieve:
① CTE matching degree ↑95%: the thermal expansion coefficient is reduced to 8×10⁻⁶/℃, which is perfectly compatible with the metal parts of the fuel system;
② Improved tensile strength: reaching 380MPa, 2 times higher than traditional aluminum alloys;
③ Breakthrough in temperature resistance limit: long-term working temperature is increased to 260℃ (traditional materials are only 150℃).
(2) Performance comparison table
| Index | Traditional aluminum alloy | LS silicon carbide magnesium-based composite material |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal expansion coefficient (10⁻⁶/℃) | 23.6 | 8.0 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 160 | 380 |
| Solvent resistance (gasoline immersion) | 0.5% swelling after 500 hours | No swelling after 1500 hours |
| Fatigue life (number of cycles) | 400,000 times | 2 million times |
4. System-level solution: design optimization and intelligent operation and maintenance
(1) Thermal deformation compensation algorithm model
① Real-time monitoring: Dynamically track the shell heat distribution through temperature sensors;
② Intelligent prediction: AI algorithm automatically compensates for the impact of deformation on oil supply pressure;
③ Active warning: Identify potential risks in advance to avoid sudden failures.
(2) Maintenance recommendations
① Clean the heat dissipation channel regularly to prevent local overheating;
② Use professional tools to detect shell deformation;
③ Select low-corrosive fuel to reduce material degradation.

Conclusion
The reliability of hydraulic valves and fuel pumps directly determines the life and death of aircraft. From low-temperature hysteresis effect to seal failure, from electromagnetic interference to fatigue cracks, behind each case is the fatal shortcomings of design, materials and processes. LS has reduced the failure rate by more than 90% with innovative solutions such as low-temperature adaptive technology (LAT) and super wear-resistant silicon carbide seals (SCS). It has also passed AS9100D certification and global 24/7 technical support to build a triple line of defense for aviation safety – material innovation to eliminate hidden dangers, intelligent monitoring to predict risks, and rapid response to minimize losses. In the face of the eight “hidden killers”, choosing LS is not only a trust in technology, but also a reverence for life. Let every takeoff become the starting point of a safe journey.
📞 Phone: +86 185 6675 9667
📧 Email:info@longshengmfg.com
🌐 Website: https://www.longshengmfg.com/
🔔Subscription Guide-Scroll to the bottom of the website, enter your email address, and click √Subscribe
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. LS makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through LS’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please contact to our for more information.
Team LS
This article was written by various LS contributors. LS is a leading resource on manufacturing with CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, injection molding,metal stamping and more.







