Aluminum extrusion is a transformative manufacturing process that reshapes aluminum alloy into definitive profiles with a fixed cross-sectional area. This process leverages the unique combination of aluminum’s physical characteristics, such as its lightweight, strength, malleability, and corrosion resistance, to create parts and structures used in various industries.
The process involves heating an aluminum billet and forcing it through a shaped opening in a die using a hydraulic press or ram. The aluminum flows and takes the shape of the die, resulting in a continuous length of aluminum with the desired cross-sectional profile. This technique capitalizes on aluminum’s malleability, making it easily formed, machined, and cast.
Significance in Various Industries
Aluminum extrusion has become an indispensable component in many industries due to its versatility and the unique properties of aluminum. Here are some examples:
-
Automotive Industry: Aluminum extrusions are extensively used in the automotive industry to create lightweight and energy-efficient vehicles. For instance, the aluminum-intensive frame of the C8 Corvette is primarily made of extruded aluminum, demonstrating the material’s significant role in modern car manufacturing.
-
Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry also benefits from aluminum extrusion. The strength-to-weight ratio of aluminum, combined with its corrosion resistance, makes it an ideal material for various aerospace parts.
-
Construction Industry: Aluminum extrusions are used for elements like guide rails, paneling, and lighting fixtures in the construction industry. Its durability and aesthetic appeal make it a popular choice for architectural applications.
-
Electronics Industry: The electronics industry uses aluminum extrusions in heat sinks, casings, and other components. Aluminum’s excellent thermal and electrical conductivity properties make it ideal for these applications.
-
Renewable Energy Industry: In the renewable energy sector, particularly in solar panel installations, aluminum extrusions create durable and lightweight mounting structures.
The versatility and benefits of aluminum extrusion, combined with the cost-effectiveness of the process, make it a preferred choice for manufacturers across these and many other industries.
Definition and Description of the Aluminum Extrusion Process
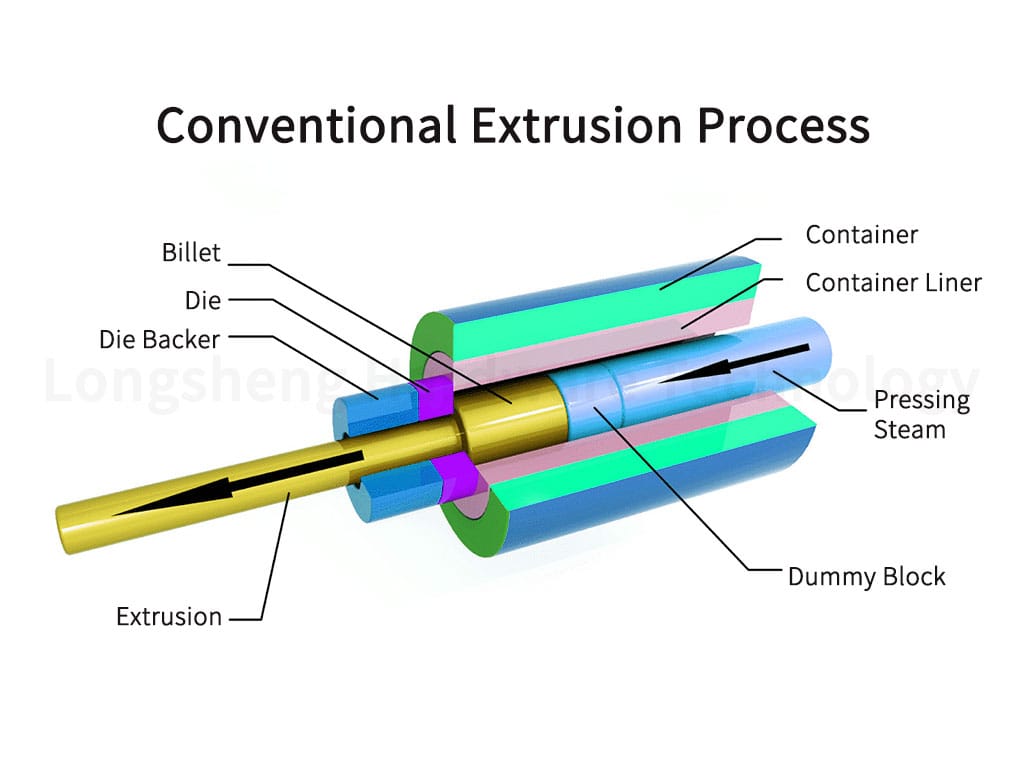
Aluminum extrusion is a manufacturing process that involves reshaping aluminum alloy into objects with a specific cross-sectional profile. This transformation is achieved by forcing the aluminum through a die-shaped opening. The process can create lengths of aluminum with complex cross-sections and excellent strength and finish. Extruded aluminum has various applications across industries due to its remarkable properties, simplifying fabrication assembly while improving strength and stiffness.
Advantages of Using Aluminum for Extrusion
Aluminum is a favored material for extrusion due to its exceptional properties. Here are some of the main advantages of using aluminum for extrusion:
-
Lightweight yet Strong: Aluminum parts might not be as strong as steel but weigh much less. This excellent strength-to-weight ratio makes handling or supporting aluminum products easier without significantly decreasing application performance.
-
Corrosion-Resistant: Aluminum naturally resists corrosion, reducing the need for unique treatments and making it suitable for applications exposed to weather or corrosive environments.
-
Excellent Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum’s high thermal and electrical conductivity makes it ideal for applications that require heat dissipation or electrical transmission.
-
Cost-Effective: Aluminum is less expensive than other metals, and the extrusion process is relatively inexpensive. Extrusion dies are far less costly than those for molding or casting and can be produced in less time.
-
Recyclable and Sustainable: Aluminum can be reused multiple times without losing its characteristics. Extrusions are often produced with high recycled content, which does not compromise aesthetics or functionality, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
-
Versatile: Aluminum’s malleability allows for easy machining, making it easy and relatively inexpensive to shape, even into complex geometries. Extrusion gives it whatever cross-section is desired, which can incorporate a host of valuable features.
These advantages make aluminum extrusion a preferred choice for manufacturers across various industries, from construction and automotive to electronics and aerospace.
Preparing for Extrusion
The preparation for the aluminum extrusion process involves crucial steps that significantly impact the final product’s quality and characteristics. These steps primarily include the selection of the appropriate aluminum alloy and controlling the billet’s temperature.
Importance of Alloy Selection
The selection of the aluminum alloy is a critical step in the extrusion process. Different alloys possess varying properties, including strength, malleability, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. These properties influence the alloy’s extrudability, how easily it can be extruded, and the mechanical characteristics of the final product. For instance, a higher-strength alloy may require more energy for extrusion but can result in a more robust and durable extruded profile. Therefore, the alloy selection must align with the desired properties and application of the final product.
Role of Billet Temperature
The temperature of the aluminum billet plays a vital role in the extrusion process. The billet is heated before extrusion to ensure it is soft enough to be forced through the die. The temperature must be carefully controlled to achieve optimal malleability without causing the aluminum to melt. If the billet’s temperature is too low, the extrusion process may require higher pressure, making the process more energy-intensive and potentially affecting the quality of the extruded profile. Conversely, if the billet’s temperature is too high, it may lead to defects in the extrusion, such as surface cracking or internal ruptures. Therefore, precise control of the billet temperature is crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of the aluminum extrusion process.
The Extrusion Process
The aluminum extrusion process involves several steps, each of which plays a crucial role in determining the quality and characteristics of the final product. Here’s a step-by-step guide through the process:
-
Preparation of the Extrusion Die: The die, which determines the cross-sectional shape of the extruded profile, is prepared and preheated to 450-500 degrees Celsius. This preheating helps maximize the die’s life and ensure even metal flow.
-
Billet Preheating: An aluminum billet is preheated in an oven to 400-500 degrees Celsius. This heating makes the billet malleable enough for extrusion but keeps it from becoming.
Post-Extrusion Treatments
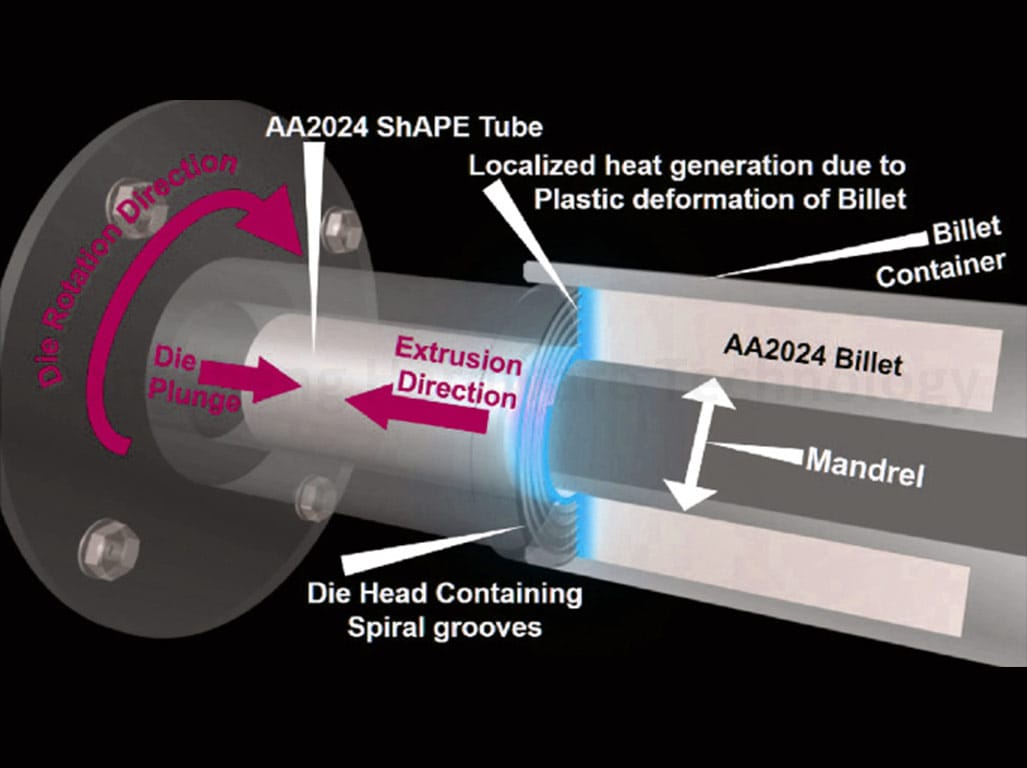
After the aluminum has been extruded through the die, it undergoes several post-extrusion treatments to solidify and strengthen the extruded profiles. These treatments are essential for enhancing the mechanical properties of the extruded aluminum and preparing it for its intended application.
Cooling and Quenching Techniques
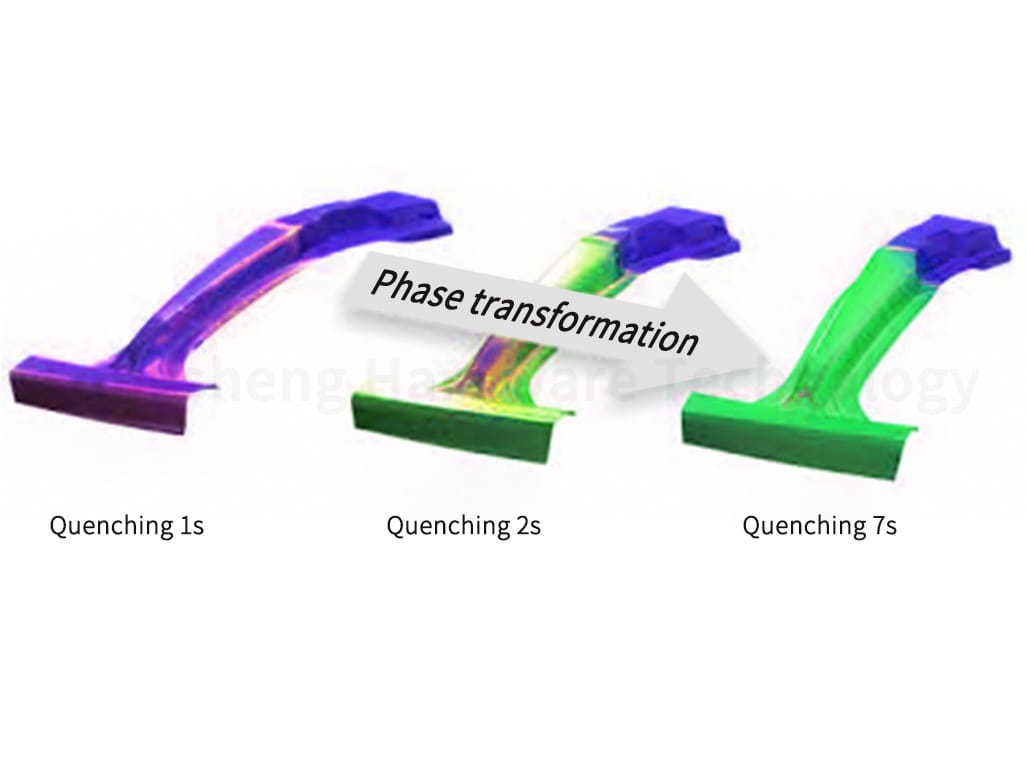
Immediately after extrusion, the aluminum profile is cooled to solidify and preserve its shape. This cooling process often involves air or water quenching, which rapidly reduces the temperature of the aluminum to prevent undesired low-temperature processes, such as phase transformations, from occurring. Quenching can also enhance the hardness of the aluminum profile, making it more durable and resistant to wear.
Stretching, Straightening, and Work Hardening
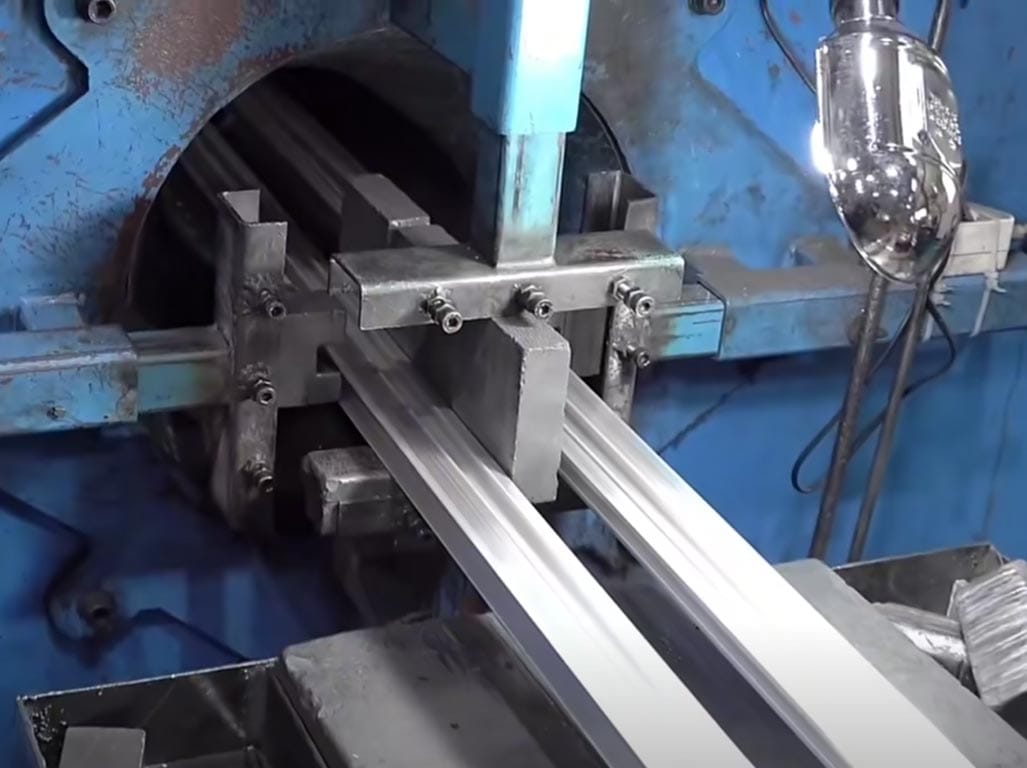

After cooling and quenching, the extruded profiles may undergo a stretching process. This process involves applying tension to the profiles to align the grains in the aluminum, which can enhance the material’s strength and ensure that it is straight. Stretching also helps to relieve internal stresses in the aluminum that may have been introduced during the extrusion process.
Straightening is another necessary post-extrusion process. Despite the precision of the extrusion process, the profiles may not always come out perfectly straight. Therefore, they are often straightened mechanically to meet the required specifications.
Work hardening, also known as strain hardening, is a process that involves deforming aluminum to increase its hardness and strength. This deformation introduces dislocations in the aluminum’s crystal lattice, which hinder the movement of other dislocations and make the material stiffer and more robust.
These post-extrusion treatments ensure that the extruded aluminum profiles have the desired properties and are suitable for their intended applications. They allow for producing high-quality aluminum products that meet the stringent requirements of various industries.
Designing for Extrusion
Designing for extrusion involves considering various factors to ensure cost and process efficiency. The design of the extrusion profile can significantly impact the ease of manufacturing, the quality of the final product, and the overall cost of the extrusion process.
Designing Extrusion Profiles for Efficiency
When designing extrusion profiles, it’s essential to consider the following points:
-
Uniform Wall Thickness: Aim for a consistent thickness in your extrusion design. Variations in thickness can cause the material to flow and cool at different rates, leading to distortion in the final profile. Uniform wall thicknesses are more accessible to manufacture and can reduce production costs.
-
Avoid Abrupt Transitions: If changes in wall thickness are unavoidable, make them gradual rather than abrupt variations. The material tends to flow faster where thicker sections occur, leading to potential distortion in the extruded shape.
-
Consider Corner Radii: Extrusion processes cannot achieve sharp corners without additional fabrication. Internal corners should be filleted with a minimum radius of 0.5-1mm, and sharp external edges should be rounded as those tips can quickly become wavy and uneven.
-
Opt for Solid Profiles: Solid profiles can reduce die costs and are often easier to produce. They are also more robust and less prone to warping or distortion.
Tips for Creating Symmetrical Shapes, Maintaining Uniform Wall Thicknesses, and Streamlining Transitions
-
Symmetrical Shapes: Symmetrical shapes are generally easier to extrude and less likely to warp or distort during cooling. They also tend to provide more uniform strength and stiffness characteristics.
-
Maintaining Uniform Wall Thicknesses: As mentioned earlier, keeping uniform wall thicknesses can help ensure consistent flow and cooling rates during extrusion. This can lead to higher-quality profiles and lower production costs.
-
Streamlining Transitions: Gradual transitions in wall thickness can help prevent distortion and ensure a more consistent material flow during extrusion. Avoid abrupt changes in wall thickness whenever possible.
By considering these factors during the design process, you can create extrusion profiles that are cost-effective, efficient to manufacture, and suitable for their intended applications.
The Role of Pressure and Speed
In the aluminum extrusion process, both pressure and speed play significant roles in determining the final product’s quality and the production process’s efficiency.
Impact of Pressure on the Quality and Consistency of the Extruded Profiles
The pressure applied during the extrusion process directly affects the quality and consistency of the extruded profiles. High pressure ensures that the aluminum fills the die and accurately takes on its shape, resulting in profiles with precise dimensions and a smooth surface finish.
However, applying too much pressure can lead to defects such as surface cracking or internal ruptures. Conversely, the aluminum may not fill the die if the pressure is too low, leading to incomplete or inconsistent profiles. Therefore, it’s crucial to carefully control the pressure to achieve the best possible quality and consistency in the extruded profiles.
How Extrusion Speed Affects the Production Process and the Final Product
The speed of the extrusion process can also significantly impact both the production process and the final product. As the extrusion speed increases, the rate at which the aluminum is forced through the die increases. This can lead to a higher production rate, potentially reducing the cost per unit of the extruded profiles.
However, increasing the extrusion speed can also affect the quality of the final product. For instance, if the speed is too high, the aluminum may not have enough time to fill the die fully, leading to incomplete or inconsistent profiles. Additionally, higher extrusion speeds can result in higher temperatures, which can affect the mechanical properties of the aluminum and potentially lead to defects such as warping or distortion.
Therefore, it’s essential to carefully control the extrusion speed to balance high production rates with the need for high-quality, consistent extruded profiles.
Finishing and Quality Control
After the extrusion process, the aluminum profiles undergo various finishing processes to enhance their functionality and aesthetics. These processes include cutting, machining, and surface finishing.
Cutting, Machining, and Surface Finishing Techniques
Cutting: The extruded profiles are cut to the required lengths using various cutting techniques. The choice of cutting method depends on factors such as the profile’s size and shape, the required precision, and the production volume.
Machining: Machining processes such as milling, drilling, and turning may add features to the extruded profiles that cannot be achieved through extrusion alone. These features can include holes, slots, and complex contours.
Surface Finishing: Surface finishing techniques enhance the extruded profiles’ texture, appearance, and performance. These techniques can include mechanical processes such as grinding, polishing, honing, and lapping, which remove material from the surface to achieve the desired finish. The selection of the appropriate surface finish parameter for a particular application depends on the function of the surface. Understanding these parameters and their implications is crucial for designing and manufacturing effective and reliable products.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control measures are essential to ensure the extruded products meet the specified tolerances and standards. These measures can include visual inspections, dimensional checks, and tests of the material’s mechanical properties.
The main objective of quality control is to ensure that goods are produced according to buyer/customer requirements. This includes maximizing the production of goods within the specified tolerances correctly the first time. The quality of the final inspection should be superior, and the quality of the sales also has to be maintained.
In some applications, such as in the aerospace industry, surface texture can be critical to the functionality and performance of the material. For example, a rough surface may be necessary to promote bonding between materials or to increase surface area for heat transfer.
As a product designer and engineer, it’s important not to control the surface roughness or characteristics on a drawing or product specification unless it is critical to its functional performance or quality. Needless surface specification increases manufacturing costs.
In conclusion, the finishing and quality control processes are crucial in producing high-quality, functional, and aesthetically pleasing extruded aluminum profiles. By carefully selecting and controlling these processes, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the stringent requirements of various industries.
Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion is a versatile and highly efficient manufacturing process with applications in various industries due to its outstanding performance, high formability, and excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
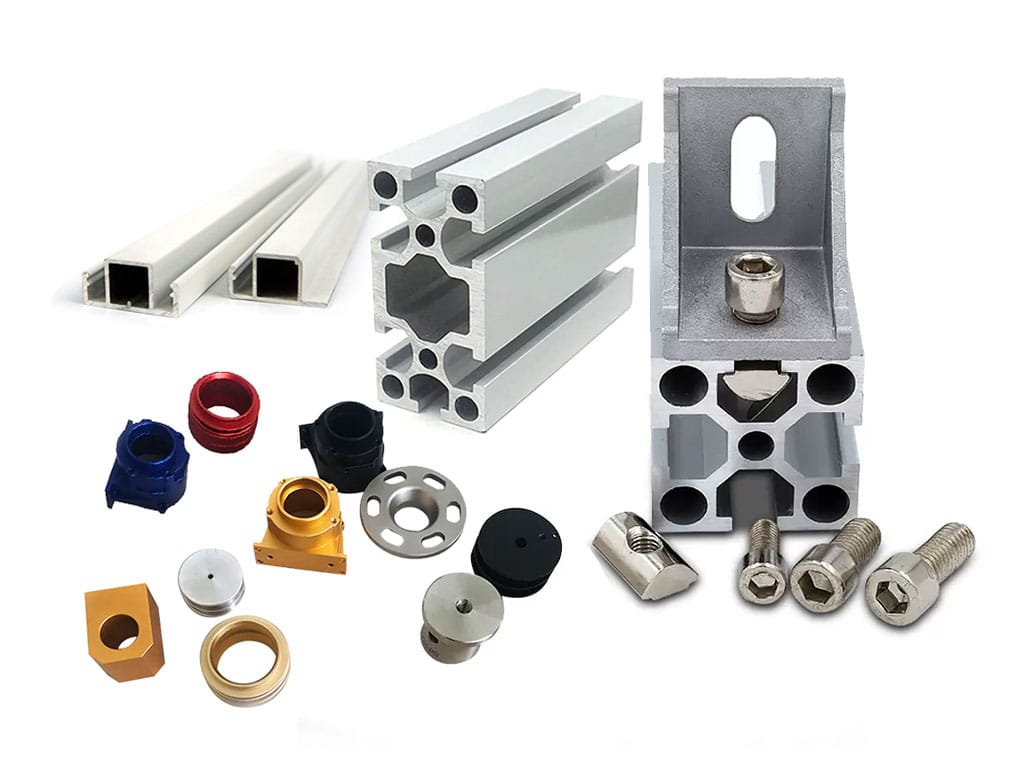

Construction Industry
In the construction industry, aluminum extrusions are widely used for their strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance. They are used to fabricate window and door frame systems, curtain walls, solar panels, and various structural components. The ability to create complex cross-sectional profiles makes aluminum extrusions ideal for many architectural applications.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has increasingly turned to aluminum extrusions to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency without sacrificing safety or performance. Extruded aluminum components can be found in various vehicle parts, including the chassis, body structure, and engine components. The use of aluminum extrusions in the automotive industry is expected to grow due to the rising demand for lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, aluminum extrusions produce many components, including heat sinks that help dissipate heat from electronic devices, frames for LED lighting, and enclosures for various electronic equipment. The excellent thermal conductivity of aluminum, combined with the ability to create complex shapes through extrusion, makes it an ideal material for these applications.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry also makes extensive use of aluminum extrusions in the production of aircraft and spacecraft components. These components must be lightweight yet extremely strong and durable, and aluminum extrusions fit these requirements perfectly. They are used to construct airframes, engine components, and various interior parts.
In conclusion, aluminum extrusion is an essential manufacturing process in many industries due to its versatility, efficiency, and the unique properties of aluminum. By selecting the appropriate alloy and extrusion process parameters, manufacturers can produce a wide range of products that meet the stringent requirements of these industries.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aluminum extrusion plays a significant role in promoting environmental sustainability due to the high recyclability of aluminum. This material can be recycled indefinitely without losing its quality or properties, significantly reducing the demand for virgin aluminum. Virgin aluminum production requires vast energy and contributes to environmental degradation, so the ability to recycle aluminum is a significant advantage for sustainability.
The aluminum extrusion industry is committed to reducing its environmental impact. This commitment includes developing, implementing, and refining business practices that advance sustainable practices throughout the value chain. The industry constantly innovates, seeking new ways to lower emissions, increase efficiencies, and strive toward a more sustainable future.
Aluminum’s low weight means you can do more with less, and it takes less energy to transport the metal from one place to another. Thanks to aluminum’s durability and resistance to corrosion, nearly 75% of all aluminum ever produced is still in use today.
The aluminum industry has made significant strides in reducing its carbon impact. Over 30 years, the North American aluminum industry has cut its carbon footprint by more than half. Companies that choose aluminum are reaping the benefits, and so is the environment. Aluminum is infinitely recyclable at the end of life, but it’s during its use phase that the material shines. Lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant, aluminum helps innovators do more with less environmental impact.
In conclusion, the recyclability of aluminum and its role in the extrusion industry significantly contribute to promoting environmental sustainability. By choosing aluminum, industries can help conserve energy and other natural resources, benefiting present and future generations.
Future Trends and Innovations
The aluminum extrusion industry is continuously evolving, with new technologies and emerging trends promising to enhance the process further and expand its applications.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
The aluminum extrusion process has undergone numerous advances and developments, resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective procedure. New technologies promise to change the process further, making it even more efficient and versatile.
One of the key trends driving the aluminum extrusion market is the global consumer shift toward fuel-efficient vehicles. This trend is expected to drive the demand for aluminum extrusions in the automotive industry as manufacturers seek to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. Using aluminum extrusions in vehicles can significantly reduce their weight, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Product innovation is another prevalent trend in the aluminum extrusion market. Manufacturers are constantly seeking to develop new products or improve existing ones to meet the changing needs of their customers. This includes the development of new alloys and extrusion techniques that can produce extruded products with improved properties, such as higher strength, better corrosion resistance, or improved thermal conductivity.
Potential New Applications and Markets
The demand for aluminum extrusions is expected to grow in various markets and applications. The increasing automotive demand is likely to drive the expansion of aluminum-rolled goods, while the growing demand for value-added and recycled aluminum goods is broadening the profitable potential for market participants.
In addition, the requirement for aluminum in new countries is opening up new markets for extruded aluminum products. These markets present significant opportunities for manufacturers to expand their operations and increase revenues.
The aluminum extrusion market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, with the global market size expected to reach a valuation of USD 1,46,202 million by 2030. This growth is driven by the increasing preference for aluminum extrusions over steel due to their outstanding performance and the growing demand for lightweight, durable, and high-corrosion-resistant extruded products.
In conclusion, the future of the aluminum extrusion industry looks promising, with numerous opportunities for growth and innovation. By embracing new technologies and trends and exploring new applications and markets, manufacturers can ensure the continued success and sustainability of the industry.
Aluminum Extrusion: An Important Manufacturing Process
The aluminum extrusion process is essential for producing parts with custom cross-sectional profiles. The process is quite interesting, and you can get various shapes of products that you can heat treat, fabricate, and finish to specification. LongSheng offers the best aluminum extrusion services for the desired result. Contact us today, and let’s bring your project to life. You can also upload your design file on our digital quotation platform for instant quotes and a transparent ordering process.
Conclusion
Aluminum extrusion has emerged as a critical process in modern manufacturing, offering a versatile and efficient method for producing a wide range of products. Its importance is underscored by its widespread use in various industries, including construction, automotive, electronics, and aerospace. The ability to create complex cross-sectional profiles, combined with the unique properties of aluminum, makes extrusion an invaluable tool for manufacturers.
The environmental impact of aluminum extrusion is also significant. Aluminum is highly recyclable, contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing the demand for virgin aluminum and conserving energy. The industry’s commitment to sustainable practices and reducing its environmental impact further underscores the importance of aluminum extrusion in today’s manufacturing landscape.
Looking ahead, the future of aluminum extrusion is promising. Emerging technologies and trends, such as the shift towards fuel-efficient vehicles and product innovation, are expected to drive growth in the aluminum extrusion market. New applications and markets are also emerging, offering exciting opportunities for the industry.
In conclusion, aluminum extrusion plays a vital role in modern manufacturing and has the potential for significant growth and innovation in the future. By embracing new technologies and exploring new applications, the industry can continue to thrive and contribute to the global economy and environmental sustainability.
FAQs
Can you explain the advantages of using aluminum extrusion?
-
Versatility: Aluminum extrusion allows for complex, multi-void hollow shapes that are difficult to produce using other methods. This versatility enables designers to form intricate shapes and profiles.
-
Strength: Extruded aluminum parts can be as strong as needed for most applications. Heat treatment can be used after extrusion to increase this strength.
-
Lightweight: Aluminum is a light metal, which makes the extruded parts lightweight. This is particularly beneficial in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where weight reduction is crucial.
-
Durability: Aluminum is corrosion-resistant, ensuring that extruded aluminum parts last longer.
-
Economical: The extrusion process is generally more economical than other shaping processes. Aluminum extrusion dies are relatively inexpensive and have a high production rate.
-
Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has good thermal and electrical conductivity properties. Extruded aluminum is often used for heat sinks in electronics and other applications that require heat dissipation.
-
Recyclability: Aluminum is highly recyclable, making aluminum extrusion environmentally friendly.
-
Finishing: Aluminum extrusions can be easily anodized, painted, or powder-coated to provide a decorative and protective finish.
Are there any limitations or challenges associated with aluminum extrusion?
-
Design Complexity: While aluminum extrusion allows for complex shapes, some design constraints remain. Not all shapes can be extruded, and the design’s complexity can impact the extrusion process’s cost and feasibility.
-
Size Limitations: There are limitations on the size of the extrusions that can be produced, both in terms of the maximum size that can be extruded and the minimum wall thickness that can be achieved.
-
Material Waste: Although aluminum is recyclable, extrusion can still generate waste material, mainly when producing complex profiles.
-
Surface Finish: While aluminum can be quickly finished, the extrusion process can sometimes result in surface imperfections that must be addressed in post-processing.
-
Heat Treatment: If increased strength is required, the extruded parts may need heat treatment, which adds to the overall production time and cost.
-
Tooling Costs: While aluminum extrusion dies are generally lower than other processes, there can still be significant tooling costs for complex profiles.
What factors should be considered when designing for aluminum extrusion?
-
Profile Design: The complexity of the profile can significantly impact the cost and feasibility of the extrusion process. Simple shapes are easier and cheaper to extrude than complex ones.
-
Wall Thickness: Uniform wall thickness is recommended to avoid distortion during the cooling process. If varying wall thickness is required, a gradual transition should be used.
-
Material Selection: Different aluminum alloys have different properties and are suitable for other applications. The choice of material can affect the final product’s strength, corrosion resistance, and finish.
-
Tolerances: Tolerances should be as generous as possible. Tight tolerances can increase the cost of the extrusion process and may not always be achievable.
-
Tooling Design: The design of the extrusion die can impact the quality of the final product. It’s essential to work with experienced tooling designers.
-
Finishing Requirements: The type of finish required (e.g., anodizing, painting, powder coating) can impact the design. Some finishes may require specific design features.
-
Heat Treatment: If the extruded parts require additional strength, heat treatment may be necessary. This can impact the cost and timeline of the project.
-
Cost Considerations: The cost of the extrusion process can be affected by the design, material selection, tooling, and finishing requirements. Considering these factors during the design phase ensures a cost-effective process.


