Lathe tools are old yet diverse machinery tools unique to lathing operations in part manufacturing. There are several types of lathe tools, each with distinct structures, material makeup, functions, etc., resulting in different applications.
The part quality is achievable with different turning tools depending on your understanding of their designs, properties, and functions. Hence, this article discusses the classifications of varying cutting tools used in lathe machines and how to choose the right one.
What is a Lathe Machine?
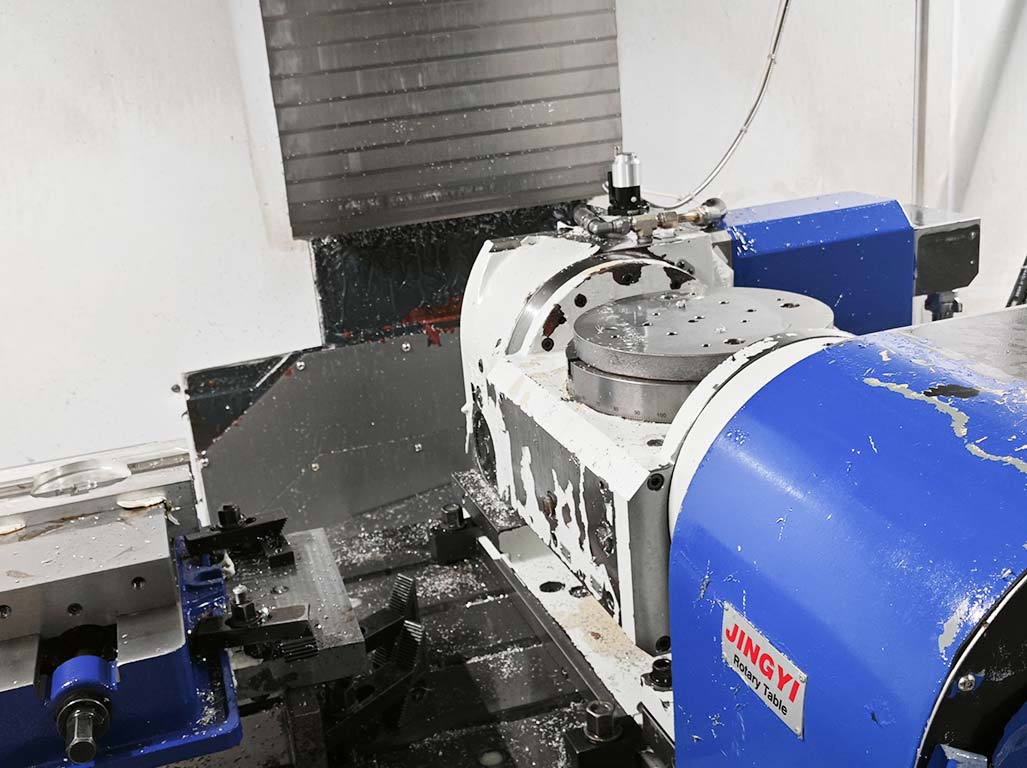

A lathe machine is a tool used in metalworking, woodworking, and other manufacturing processes to rotate a workpiece about an axis of rotation. The primary function of a lathe is to remove material from the workpiece to form it into a specific shape or design.
The machine holds the workpiece in place while it is rotated, and a cutting tool is then applied to the workpiece to cut, sand, drill, or deform it into the desired shape. The cutting tool can move in two directions – along the axis of rotation for a longitudinal cut or perpendicular to the axis for a facing cut.
There are several types of lathe machines, including engine lathes, turret lathes, and CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes. Each type has its specific uses and applications.
Lathe-cutting tools are integral to CNC (Computer Numerical Control) operations. They are used to cut, shape, and finish materials in various manufacturing and engineering applications. Here are some reasons why they are essential:
-
Precision and Accuracy: Lathe cutting tools are responsible for the precision and accuracy of the machining process. They allow for creating complex shapes and designs with high precision, which would be difficult to achieve manually.
-
Versatility: There are several types of lathe-cutting tools, including turning tools, boring tools, parting tools, and threading tools, among others. Each tool has a specific purpose and performs different operations, making the CNC machine versatile.
-
Efficiency: CNC technology allows for greater control over the machining process. The computer-controlled nature of these machines means that they can produce consistent, high-quality results faster than manual methods.
-
Cost-Effective: While the initial investment in CNC machines and lathe-cutting tools can be high, their efficiency and precision can lead to cost savings in the long run. They reduce waste and the need for manual labor, which can be more expensive in the long term.
-
Consistency: with the help of lathe-cutting tools, CNC machines can produce identical parts repeatedly with minimal variation. This is crucial in industries where consistency and standardization are key.
Types of Lathe Cutting Tools
Lathe cutting tools are essential components in CNC machines, and they come in various types, each designed for specific operations. Here are the main types of lathe-cutting tools used in CNC machines:
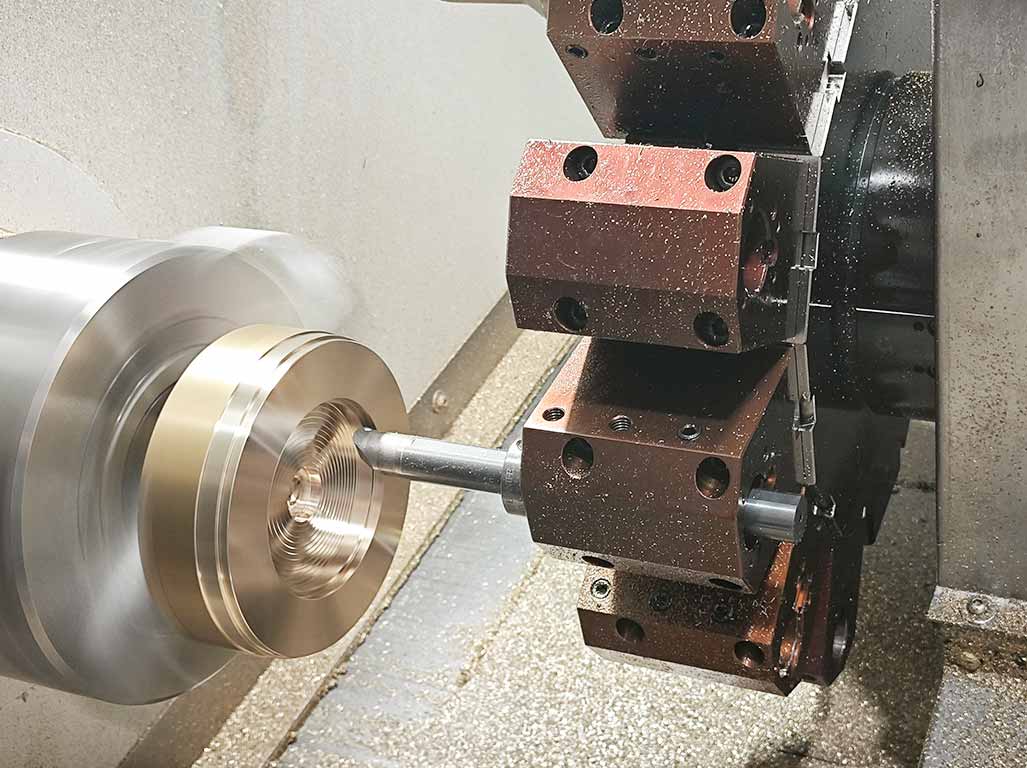
1. Turning Tools: These are the most commonly used lathe-cutting tools. They remove material from the workpiece, creating a cylindrical shape. Turning tools can be further classified into straight, taper, and form turning tools, each used for different turning operations.

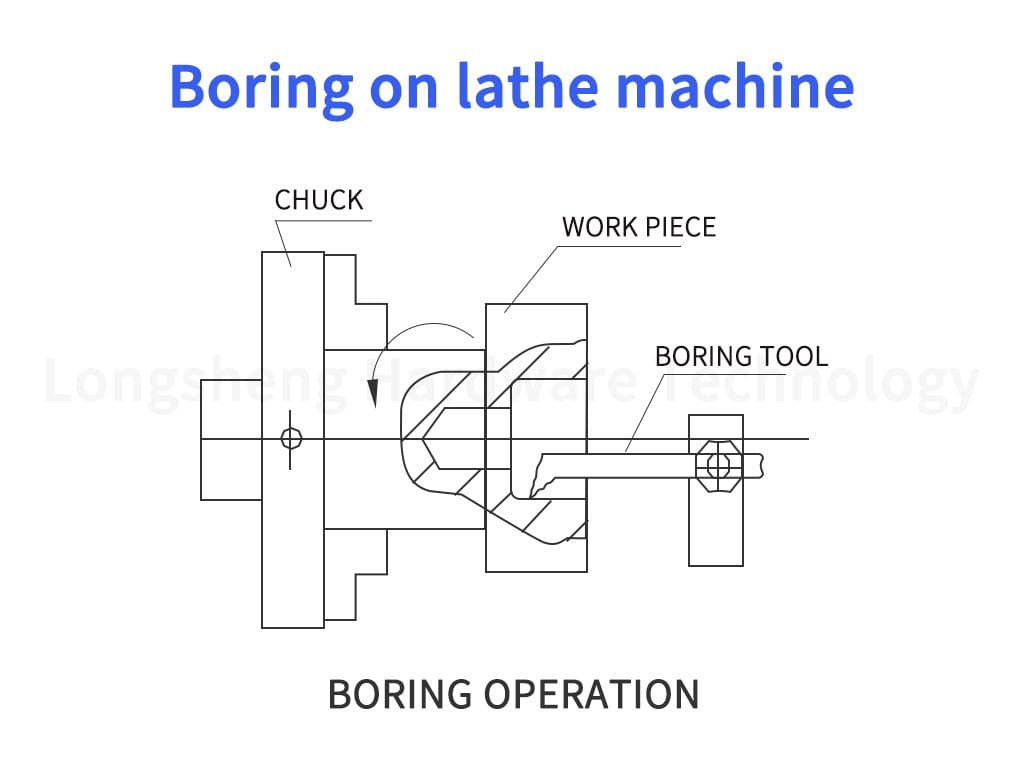
2. Boring Tools: Boring tools enlarge an already drilled hole. They are typically employed when the precision of the hole diameter is required. Boring tools can be single-point or multi-point tools.

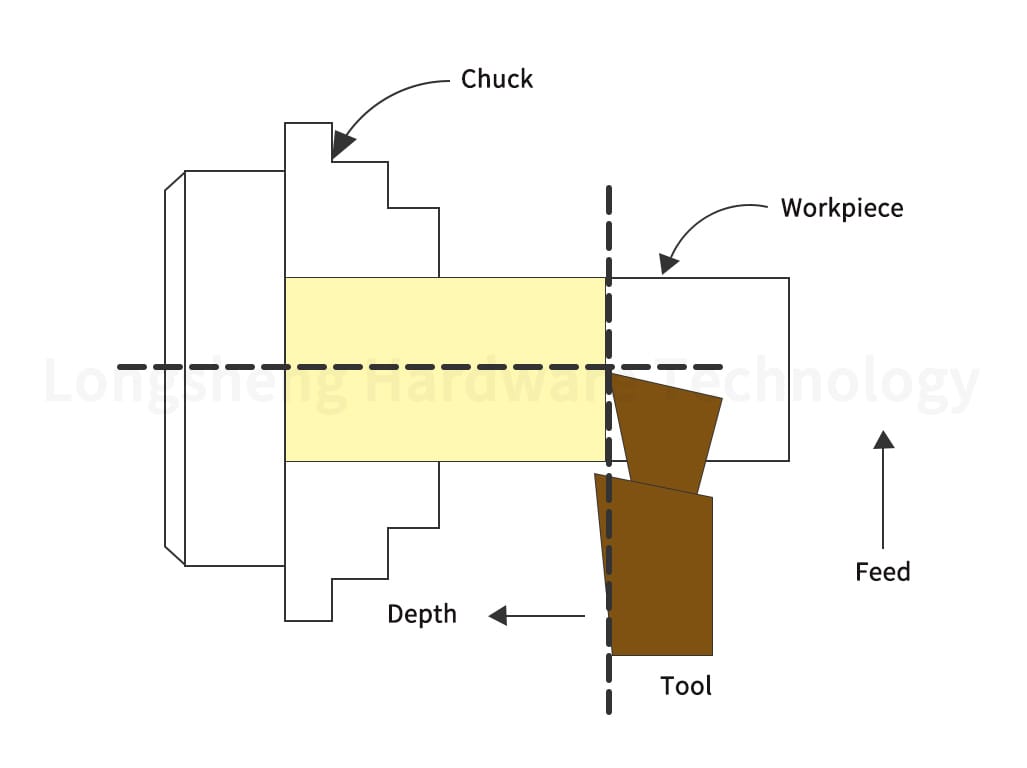
3. Parting Tools: Parting tools, also known as cut-off tools, are used to cut off a portion of the workpiece after achieving the desired shape. They are thin and are utilized to make deep cuts. Parting tools must be sharp and rigid to prevent bending or breaking during cutting.

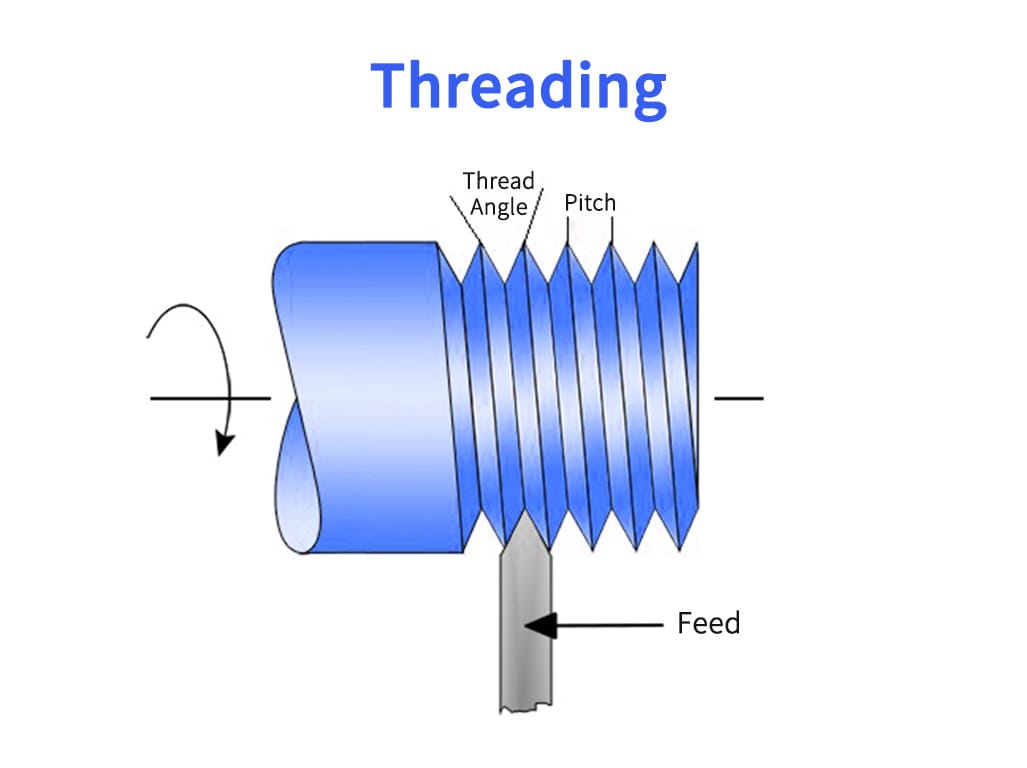
4. Threading Tools: Threading tools create threads on the workpiece. They have a pointed nose and are utilized to cut both internal and external threads. Threading tools can be used for different threads, including metric, Whitworth, and Acme threads.
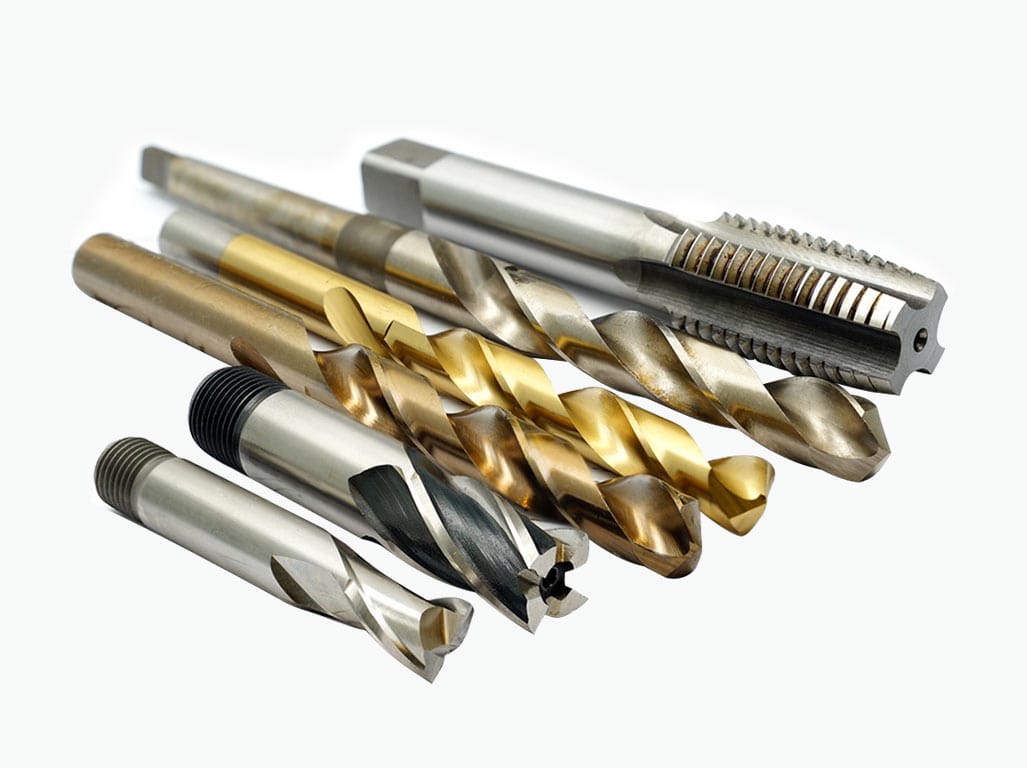

5. Drilling Tools: Drilling tools create holes in the workpiece. They are typically utilized in conjunction with a tailstock. Drilling tools can be used for different drilling operations, including center drilling, deep hole drilling, and trepanning.

6. Knurling Tools: Knurling tools produce a regular pattern of fine, straight, angled, or crossed lines on the workpiece. This is typically done to provide a better grip on the finished part.

7. Facing Tools: Facing tools create a flat surface at the end of the workpiece. They are typically used in conjunction with a carriage.

Applications of Lathe Cutting Tools
Lathe-cutting tools are used in various industries for various applications. Here are some of the critical industries and applications:
-
Manufacturing Industry: In the manufacturing industry, lathe-cutting tools produce parts and components with complex shapes and high precision. They are used in making automotive parts, aerospace components, and machinery parts.
-
Metalworking: In metalworking, lathe-cutting tools are used for turning, boring, parting, threading, and drilling operations. They are utilized to shape metal pieces into desired forms.
-
Woodworking: In woodworking, lathe-cutting tools shape wood into various forms, such as bowls, spindles, and furniture. They are used for turning, facing, and parting wood pieces.
-
Plastic Industry: In the plastic industry, lathe-cutting tools shape plastic materials into various forms. They are used in the production of plastic components for multiple applications.
-
Construction Industry: In construction, lathe-cutting tools produce construction materials and components. They are used to shape and finish materials utilized in construction.
-
Jewelry Industry: In the jewelry industry, lathe-cutting tools are used to shape and design jewelry pieces with high precision and detail.
-
Medical Industry: In the medical industry, lathe-cutting tools produce medical devices and equipment. They are used to make components with high precision and accuracy.
Lathe Cutting Tools for CNC Machines
Lathe-cutting tools are integral to the operation of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines. CNC machines are automated machining tools that produce exact and consistent parts. Here’s an in-depth look at how lathe-cutting tools are used in CNC machines:
1. Programming and Control: In CNC machines, the movements and operations of the lathe cutting tools are controlled by a computer program. This program dictates the cutting path, depth of cut, feed rate, and other parameters. The operator only needs to set up the machine and load the program; the machine does the rest.

2.Turning Operations: One of the primary uses of lathe-cutting tools in CNC machines is for turning operations. Turning tools remove material from the workpiece, creating a cylindrical shape. The CNC machine can control the depth of cut and feed rate to achieve the desired shape and finish.

3. Boring Operations: Boring tools are used in CNC machines to enlarge an already drilled hole. The CNC machine can control the hole’s diameter and the cut depth to achieve high precision.
4. Parting Operations: Parting tools are used in CNC machines to cut off a portion of the workpiece after the desired shape has been achieved. The CNC machine can control the depth of the cut to ensure a clean and precise cut.
5. Threading Operations: Threading tools are used in CNC machines to create threads on the workpiece. The CNC machine can control the pitch and depth of the threads to ensure consistency and precision.
6. Drilling Operations: Drilling tools are used in CNC machines to create holes in the workpiece. The CNC machine can control the diameter and depth of the hole to achieve high precision.
Choosing the Right Lathe Cutting Tool
Selecting the right lathe-cutting tool for specific CNC machine applications can significantly impact the output quality and the process’s efficiency. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a lathe-cutting tool:
-
Material of the Workpiece: The type of material you work with significantly determines the appropriate cutting tool. More complex materials require more robust and durable tools, while softer materials can be performed with less sturdy tools. For example, carbide tools are suitable for more complicated materials like steel, while high-speed steel (HSS) tools can be used for softer materials like aluminum.
-
Type of Operation: The operation you intend to perform also influences the choice of the tool. For instance, you’ll need turning tools if you do turning operations. If you’re going to do threading, you’ll need threading tools, and so on.
-
Size and Shape of the Workpiece: The size and shape of the workpiece can also dictate the type of tool required. Larger workpieces may require more extensive tools, while smaller or more intricate ones may need smaller, more precise ones.
-
Machine Compatibility: Not all tools are compatible with all CNC machines. Ensure the tool you choose is compatible with your machine in size, mounting style, and other specifications.
-
Quality of the Tool: The quality of the tool is crucial for achieving high-quality results. High-quality tools are typically made from durable materials that provide precise and consistent results.
-
Cost: While choosing high-quality tools is important, it’s also essential to consider the cost. More expensive tools often offer better performance and longevity, but they may not always be necessary for every application.
Maintenance and Care for Lathe Cutting Tools
Proper maintenance and care for lathe-cutting tools are crucial to ensure their longevity and efficiency. Here are some tips and best practices:
-
Regular Cleaning: After each use, clean the tools to remove debris or cutting fluid. This can prevent rust and keep the tools in good condition.
-
Proper Storage: Store the tools in a dry and clean place. Avoid leaving them in a damp or dirty environment, which can cause rust or damage.
-
Regular Inspection: Inspect the tools for any signs of wear or damage. If you notice any issues, address them immediately to prevent further damage.
-
Proper Usage: Use the tools for their intended purpose and avoid using them for tasks they are not designed for. This can prevent unnecessary wear and tear.
-
Sharpening: Keep the tools sharp. Dull tools can cause poor-quality cuts and put more strain on the machine. Use a tool grinder or a sharpening service to keep your tools strong.
-
Lubrication: Some tools may require regular lubrication to keep them functioning smoothly. Check the manufacturer’s instructions for specific lubrication requirements.
-
Handle with Care: Handle the tools with care to prevent damage. Avoid dropping them or knocking them against hard surfaces.
-
Professional Maintenance: Consider professional maintenance services for complex tools or if you are unsure how to maintain them. They can ensure your tools are properly cared for and can help extend their lifespan.
Innovations and Future Trends in Lathe Cutting Tools
The field of lathe-cutting tools for CNC machines continuously evolves, with new technologies and trends emerging regularly. Here are some of the key innovations and future trends:
-
Advanced Materials: Developing advanced materials for lathe-cutting tools is a significant trend. These materials, such as cubic boron nitride (CBN) and polycrystalline diamond (PCD), offer superior hardness and heat resistance, allowing faster cutting speeds and longer tool life.
-
Coating Technologies: Advances in coating technologies are enhancing the performance of lathe-cutting tools. Coatings such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) can increase tool life, improve surface finish, and allow for higher cutting speeds.
-
Intelligent Tools: Integrating sensors and connectivity in lathe-cutting tools is a growing trend. These “smart” tools can monitor their condition and performance in real-time, providing valuable data for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
-
3D Printing: Using 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, to produce lathe-cutting tools is an emerging trend. This technology allows for creating tools with complex geometries and customized designs, potentially improving performance and efficiency.
-
Sustainability: As sustainability becomes increasingly important, there is a growing focus on developing more energy-efficient tools and processes and tools made from recycled or environmentally friendly materials.
-
Automation and AI: The increasing use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in CNC machining will likely impact the field of lathe-cutting tools. These technologies can optimize tool paths, adjust cutting parameters in real-time, and even predict tool wear, improving efficiency and quality.
Case Studies
Case Studies: Use of Lathe Cutting Tools in CNC Machines Across Various Industries
-
Automotive Industry: CNC machines with lathe-cutting tools are extensively used for producing engine parts, such as pistons and cylinder heads. For instance, turning tools are utilized to shape the pistons, while drilling tools are utilized to create holes for the piston rings. The precision and consistency provided by CNC machines are crucial for ensuring the high performance and reliability of the engine.
-
Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry requires parts with complex shapes and high precision, and CNC machines with lathe-cutting tools are ideally suited for this task. For example, boring tools create precise holes in turbine blades, while threading tools make threads for fasteners. The high precision and consistency of CNC machines are vital for ensuring the safety and performance of aircraft.
-
Medical Industry: CNC machines with lathe-cutting tools produce various medical devices and implants in the medical industry. For instance, turning tools are used to shape orthopedic implants, while drilling tools are utilized to create holes for screws. The ability of CNC machines to produce parts with high precision and consistency is crucial for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
-
Electronics Industry: In the electronics industry, CNC machines with lathe-cutting tools are used to produce components for electronic devices. For example, parting tools cut off small parts after they have been shaped, while drilling tools create holes for mounting components. The precision and consistency of CNC machines are essential for ensuring the functionality and reliability of electronic devices.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Using lathe-cutting tools in CNC machines has both direct and indirect environmental impacts. Here’s a discussion on these impacts and how to utilize these tools more sustainably:
-
Material Consumption: The production of lathe-cutting tools involves consuming various materials, including metals and synthetic compounds. Overconsumption of these resources can lead to depletion and environmental degradation. Whenever possible, choosing tools made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials is essential to mitigate this.
-
Energy Use: CNC machines, including lathe cutting tools, consume significant energy during operation. This energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily if the energy is sourced from fossil fuels. To reduce energy use, consider using energy-efficient machines and optimizing machining processes to minimize energy consumption.
-
Waste Generation: Using lathe cutting tools, including metal chips and cutting fluids, generates waste. These wastes can have harmful environmental impacts if not properly managed. Implementing waste management practices, such as recycling metal chips and properly disposing of used cutting fluids, can help mitigate these impacts.
-
Tool Disposal: Lathe cutting tools eventually wear out and must be replaced. The disposal of worn-out tools can contribute to landfill waste. To address this, consider using tools with replaceable cutting edges, which reduce the amount of waste generated. Additionally, some manufacturers offer tool recycling programs.
-
Sustainable Practices: Adopting sustainable practices in CNC machining can significantly reduce the environmental impact. This includes using biodegradable cutting fluids, optimizing machining processes to lower energy use and waste generation, and implementing regular maintenance practices to extend tool life.
Meeting Modern Machining Needs with LongSheng Solutions
Are you looking for a reliable and reputable partner for your lathe tools machining needs or custom machined parts? Choose LongSheng for a top-quality experience. Upload your CAD file on our online quotation platform and get instant quotations with an automated DfM report. Furthermore, you can also manage and track your order until delivery!
At Longsheng, we deliver quality manufacturing solutions to our clients by leveraging innovative technology and experienced teams. Our team of engineers has extensive knowledge about machining tools, and our recurring use of these tools puts us at the forefront of custom machining.
Conclusion
Lathe-cutting tools play a crucial role in the operation of CNC lathe machines. They are used to perform various machining operations such as turning, drilling, boring, threading, and parting. These tools are essential in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics, where they enable the production of parts with high precision and consistency.
The field of lathe-cutting tools is continuously evolving, driven by advances in materials, technologies, and the growing importance of sustainability and digitalization. The development of advanced materials such as cubic boron nitride (CBN) and polycrystalline diamond (PCD) is enhancing the performance and longevity of these tools. At the same time, advances in coating technologies are improving tool life and cutting speeds.
Integrating sensors and connectivity in lathe-cutting tools is another significant trend. These “smart” tools can monitor their condition and performance in real-time, providing valuable data for predictive maintenance and process optimization. The use of 3D printing to produce lathe-cutting tools is also an emerging trend, allowing for the creation of tools with complex geometries and customized designs.
Looking ahead, the field of lathe-cutting tools for CNC machines will likely continue growing and innovating. The increasing focus on sustainability is expected to drive the development of more energy-efficient tools and processes and tools made from recycled or environmentally friendly materials. The growing use of automation and artificial intelligence in CNC machining is also likely to impact the field, leading to further improvements in efficiency and quality.
In conclusion, lathe-cutting tools are a vital component of CNC lathe machines, with various applications across various industries. The field is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by technological advances and a growing focus on sustainability.
FAQs
What is the difference between right-hand and left-hand lathe-cutting tools?
Right-hand and left-hand lathe cutting tools are named based on the direction of the feed during the cutting process.
-
Right-Hand Cutting Tool: A right-hand cutting tool is designed to cut the workpiece when fed from right to left. The cutting edge is on the tool’s left side, and the chip flows over the tool. This is the most commonly used type of cutting tool in a lathe.
-
Left-Hand Cutting Tool: A left-hand cutting tool cuts the workpiece when fed from left to right. The cutting edge is on the right side of the tool, and the chip flows away from the tool.
The choice between a right-hand and left-hand cutting tool depends on the machining operation and the lathe setup. It’s important to note that the terms “right-hand” and “left-hand” refer to the feed’s direction, not the operator’s hand.
Can the same lathe tool be used for different materials?
Yes, the same lathe tool can be used for different materials, but it’s essential to consider several factors:
-
Tool Material: The material of the lathe tool itself plays a crucial role. For instance, high-speed steel (HSS) tools can be used for various materials, including steel, aluminum, and plastic. Carbide tools, on the other hand, are more suitable for more complex materials like stainless steel and titanium.
-
Cutting Speeds and Feeds: Different materials require different cutting speeds and feeds. For example, softer materials like aluminum can be cut at higher speeds, while more complex materials like steel require slower speeds.
-
Tool Geometry: The shape and angle of the cutting edge, known as the tool’s geometry, can also affect its suitability for different materials. Some materials may require a sharper edge, while others may need a more robust cutting edge.
-
Coolant Usage: Some materials, especially metals, generate much heat when machining. Using a coolant can help control the temperature and extend the tool’s life.
In conclusion, while the same lathe tool can be used for different materials, it’s essential to adjust the cutting parameters and consider the tool’s material and geometry to ensure effective and efficient machining.
What is the significance of feed direction in lathe tools?
The feed direction in lathe tools is significant as it determines the direction of tool movement and the resulting surface finish on the workpiece.
-
Tool Movement: The feed direction controls the movement of the tool relative to the workpiece. In a lathe, the tool can move longitudinally (along the length of the workpiece) or transversely (across the workpiece). The direction of the feed can affect the shape and dimensions of the machined part.
-
Surface Finish: The feed’s direction also influences the workpiece’s surface finish. A longitudinal feed generally results in a smoother finish as the tool moves along the length of the workpiece, while a transverse feed can result in a rougher finish due to the tool moving across the workpiece.
-
Chip Formation: The feed direction can also affect chip formation during cutting. Different feed directions can result in various types of chips, impacting the cutting process’s efficiency and the tool’s lifespan.
-
Tool Wear: The direction of the feed can influence the wear on the cutting tool. Specific feed directions may cause more wear on certain parts of the tool, affecting the tool’s lifespan and the quality of the machined part.


