In the world of plastic manufacturing, injection molding is a widely used process that offers efficiency and precision. However, like any manufacturing technique, it is not without its challenges. Common plastic injection molding defects can arise, causing frustration and setbacks in production. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore these defects one by one, providing practical solutions to address them. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the field, this article aims to be your go-to resource for troubleshooting injection molding issues. Let’s dive in!
Introduction
Plastic injection molding defects can range from minor imperfections to major issues that compromise the quality and functionality of the final product. Addressing these defects is crucial for ensuring that your manufacturing process runs smoothly and produces high-quality parts. In this article, we will delve into various common defects, identify their root causes, and discuss effective solutions.
Understanding Common Injection Molding Defects
| Defect | Cause | Solution | |
| 1 | Short shot | Low injection pressure, insufficient melt temperature, poor mold design | Increase injection pressure, increase melt temperature, modify mold design |
| 2 | Flow line | Variations in the flow of molten plastic | Use a higher injection pressure, increase melt temperature, adjust mold design |
| 3 | Sink mark | Shrinkage of molten plastic as it cools | Use a thicker wall section, reduce injection pressure, increase melt temperature |
| 4 | Air trap | Pockets of air trapped in the mold cavity | Increase injection pressure, increase melt temperature, vent mold cavity |
| 5 | Warpage | Uneven cooling, mold shrinkage, residual stresses | Use a balanced mold design, apply uniform cooling conditions, anneal plastic part |
Table 1.1 shows some of the common Plastic Injection Molding Defects and their Solutions
Section 1: Weld Lines
Introduction
Weld lines, also referred to as knit lines or meld lines, are a frequently encountered issue in the realm of injection-molded parts. These defects manifest when two flow fronts of molten plastic converge and solidify at different times, leading to the formation of a vulnerable seam or line on the surface of the part.
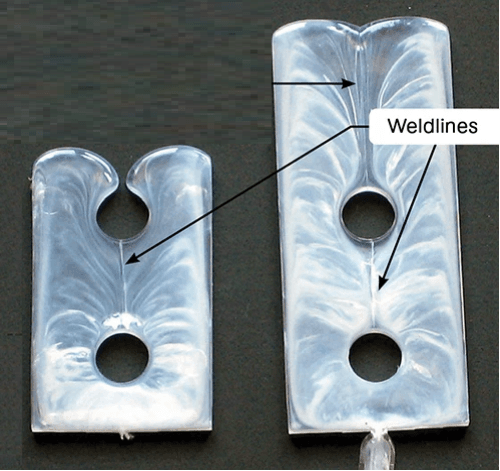
Common Causes of Weld Lines
Material Flow
Uneven material flow plays a pivotal role in the emergence of weld lines. When molten plastic fails to flow uniformly into the mold, it increases the likelihood of these defects.
Part Geometry
The complexity of part designs also contributes to the susceptibility of weld lines. Parts with varying thicknesses, intricate shapes, or intricate features are more prone to experiencing this issue.
Injection Speed
High injection speeds can exacerbate the formation of weld lines. Rapid injection can cause the plastic to cool and solidify unevenly, resulting in weaker seam lines.
Solutions to Weld Lines
Material Selection
Selecting materials with favorable flow properties is an effective strategy to mitigate weld lines. Materials that exhibit good flow characteristics can help ensure a more uniform distribution within the mold. One of the materials that exhibit good flow characteristics is Polycarbonate (PC). Polycarbonate is known for its excellent flow characteristics, making it a preferred choice for applications where avoiding weld lines is critical.
Gate Placement
Optimizing the location of the gate through which the plastic is injected into the mold is another critical step. Proper gate placement enhances material flow, reducing the likelihood of weld line formation.
Modify Part Design
Simplifying complex part geometries is a proactive approach to minimizing the risk of weld lines. Streamlining the design by reducing intricate features and variations in thickness can lead to smoother material flow and improved part quality.
By addressing these common causes and implementing these solutions, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of weld lines in your injection-molded parts, resulting in higher-quality products and more efficient manufacturing processes.
Section 2: Sink Marks
Introduction
Sink marks are a common cosmetic issue found on the surface of injection-molded parts. These marks manifest as depressions or dimples and occur due to uneven shrinkage during the cooling process. The result is visible imperfections on the part’s surface, which can impact its overall appearance.

Common Causes of Sink Marks
Cooling Rate
One of the primary culprits behind sink marks is uneven cooling rates within the mold. When different sections of the part cool at varying rates, it leads to differential shrinkage, resulting in sink marks.
Part Thickness
The thickness of different sections of the part plays a significant role in sink mark formation. Thick sections tend to cool more slowly than thinner ones, increasing the likelihood of sink marks in areas with greater material thickness.
Material Properties
The type of material used in the injection molding process can influence sink mark formation. Some materials are inherently more prone to experiencing sink marks due to their unique properties.
Solutions to Sink Marks
Gate Location
Optimizing the location of the gate, where the molten plastic enters the mold, is a key strategy for achieving uniform cooling and reducing sink marks. Proper gate placement ensures that the material flows evenly throughout the mold, minimizing differential shrinkage.
Reduce Part Thickness
To promote more uniform cooling and decrease the risk of sink marks, consider thinning out the thicker sections of the part. This modification equalizes cooling rates and reduces the chances of unsightly depressions on the surface.
Use Ribbing
Incorporating ribbing into the part design is another effective technique for addressing sink marks, especially in thick areas. Ribs act as structural reinforcements, minimizing differential shrinkage and helping to maintain a smoother surface finish.
By understanding the common causes of sink marks and implementing these solutions, you can enhance the cosmetic quality of your injection-molded parts. Achieving a more uniform surface appearance not only improves aesthetics but also contributes to the overall quality of the final product.
Section 3: Flash
Introduction
Flash is an injection molding defect characterized by the presence of excess material extending beyond the intended parting line of the mold. It occurs when molten plastic escapes from the mold cavity and solidifies outside of the designated part boundaries. Flash can negatively impact the appearance and functionality of the final product.

Common Causes of Flash
Inadequate Clamping
Insufficient mold clamping is a primary cause of flash. When the mold halves are not securely clamped together, molten plastic can seep out through the gaps, resulting in flash formation.
Excessive Injection Pressure
Overly high injection pressures can force molten plastic to escape from the mold cavities. This excessive pressure can lead to flash, particularly in areas where the mold sealing is not sufficient.
Worn Mold
The wear and tear on the mold over time can also contribute to flash formation. As molds age, they may develop imperfections or gaps that allow plastic to escape and create flash.
Solutions to Flash
Maintain Mold
Regular mold maintenance is crucial for preventing flash. Inspect molds regularly to identify and address any signs of wear or damage. Proper maintenance ensures that the mold remains in optimal condition, reducing the risk of flash.
Optimize Clamping
Ensuring proper mold clamping is essential to prevent material escape and flash formation. Properly secured mold halves create a tight seal, preventing plastic from leaking out. Regularly check and adjust clamping mechanisms to maintain effective sealing.
Reduce Injection Pressure
Adjusting injection pressure within recommended limits is another effective measure to mitigate flash. Excessive pressure can force plastic to escape, so optimizing injection parameters helps maintain control and prevent flash.
By understanding the common causes of flash and implementing these solutions, you can minimize the occurrence of this injection molding defect. A well-maintained mold, proper clamping, and controlled injection pressure contribute to producing high-quality, flash-free parts, improving both aesthetics and functionality.
Section 4: Short Shots
Introduction
Short shots represent a common challenge encountered in the realm of injection molding. These defects occur when the mold fails to completely fill with plastic during the injection molding process, resulting in parts that are incomplete or underfilled. Addressing short shots is essential for ensuring the production of fully formed and functional parts.

Common Causes of Short Shots
Insufficient Injection Pressure
Inadequate injection pressure is a primary cause of short shots. When the pressure is not sufficient to drive the molten plastic into all areas of the mold cavity, incomplete filling occurs, leading to short shots.
Material Temperature
The temperature of the plastic material used in the injection molding process can significantly affect its flow properties. Incorrect material temperature can impede the flow of plastic, resulting in incomplete filling and short shots.
Improper Venting
Proper venting is essential to allow air to escape from the mold cavity as plastic is injected. Inadequate venting can trap air within the mold, preventing complete filling and leading to short shots.
Solutions to Short Shots
Adjust Injection Parameters
Optimizing injection parameters, including pressure, temperature, and injection speed, is crucial for mitigating short shots. By fine-tuning these settings within recommended limits, you can ensure that the mold cavity is adequately filled with plastic.
Enhance Venting
Ensuring that molds have proper venting channels is essential to prevent short shots. Adequate venting allows trapped air to escape, enabling complete filling of the mold cavity. Regularly inspect and maintain venting channels to keep them clear and functional.
Gate Placement
Strategically placing gates through which the molten plastic enters the mold is another effective strategy for achieving complete filling and preventing short shots. Proper gate placement optimizes material flow and distribution within the mold cavity.
By addressing the common causes of short shots and implementing these solutions, you can enhance the quality and consistency of your injection-molded parts. Achieving complete filling of the mold cavity ensures that your parts meet design specifications and perform as intended, minimizing waste and optimizing production efficiency.
Section 5: Warpage
Introduction
Warpage is a common challenge encountered in the injection molding process. It refers to the deformation or twisting of an injection-molded part after it has cooled and solidified. This issue can lead to dimensional inaccuracies and adversely affect the functionality of the part, making it crucial to address warpage effectively.

Common Causes of Warpage
Non-Uniform Cooling
Uneven cooling within the mold is a primary cause of warpage. Differential shrinkage occurs when different sections of the part cool at varying rates. This imbalance in cooling can lead to warpage and deformation.
Material Selection
The choice of material plays a significant role in determining a part’s susceptibility to warpage. Some materials are inherently more prone to warpage due to their specific properties, such as thermal expansion coefficients.
Ejection Timing
Premature ejection of the part from the mold can cause warpage. If the part is removed before it has fully cooled and solidified, it may deform under residual stress, leading to warpage.
Solutions to Warpage
Optimize Cooling
Ensuring even cooling throughout the mold is essential for preventing warpage. This can be achieved by optimizing cooling channels, cycle times, and mold design. Uniform cooling minimizes differential shrinkage and promotes part stability.
Select Suitable Materials
Choosing materials with low warpage tendencies is a proactive step to reduce the risk of warpage. Conduct thorough material selection based on the specific requirements of your project to minimize the chances of deformation.
Adjust Ejection Timing
Delaying the ejection of the part until it has fully cooled and solidified is a critical strategy to prevent warpage. Allowing the part to remain in the mold for an adequate period ensures that it maintains its shape and integrity.
By addressing the common causes of warpage and implementing these solutions, you can significantly reduce the risk of part deformation and enhance the quality of your injection-molded products. Achieving dimensional accuracy and minimizing warpage contributes to the overall success of your manufacturing process.
Conclusion
In the world of plastic injection molding, defects are not uncommon, but they are certainly manageable. By understanding the common causes of defects and implementing effective solutions, you can enhance the quality of your injection-molded parts and streamline your manufacturing process.
Remember that the key to successful injection molding lies in continuous improvement, meticulous attention to detail, and a commitment to optimizing your processes. Whether you are dealing with weld lines, sink marks, flash, short shots, or warpage, the knowledge and strategies provided in this article will empower you to overcome these challenges and produce top-notch injection-molded products.
As you embark on your journey in the world of plastic injection molding, use this guide as a valuable reference to troubleshoot defects and achieve the best possible results in your manufacturing endeavors.
Now, armed with this knowledge, you can confidently tackle common plastic injection molding defects and elevate your production capabilities to new heights. Happy molding!
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts by injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity. Once the material cools and solidifies, it takes the shape of the mold, creating a finished plastic product.
Sink marks occur when the cooling rate of the plastic is not uniform throughout the part, causing uneven shrinkage. This non-uniform shrinkage leads to depressions or dimples on the part’s surface.
To prevent flash, you can optimize mold design, adjust clamping force, and fine-tune process parameters like injection speed and pressure. Proper maintenance of the mold is also crucial to minimize flash.
Warping and distortion can result from non-uniform cooling, excessive residual stress, or inadequate part design. Proper mold and part design, along with optimized processing parameters, can help prevent these issues.
Numerous injection molding defects, as mentioned earlier, can mar the appeal of your molded parts and wreak havoc on your bottom line. Fortunately, there are proactive steps you can take to prevent many of these issues by embracing meticulous design processes. Some defects can be rectified with alterations to the materials used and more appropriate storage conditions.That’s why making a substantial upfront investment in tooling is essential for this process. Getting your mold design right from the outset is paramount. This is where Longsheng Hardware Technology Co., Ltd. steps in to be your trusted partner!
At Longsheng Hardware Technology Co., Ltd., we are seasoned professionals, dedicated to delivering top-tier Plastic Injection molding services. We possess a deep understanding of various injection molding defects and their root causes. With our cutting-edge technical expertise, we leave no stone unturned in preventing these defects.
Our cost-efficient plastic injection molding services cater to both mass production and rapid prototyping needs. When you entrust us with your design files for a quotation, you’re in for a world of benefits, including these and more. Make the smart choice by partnering with Longsheng Hardware Technology Co., Ltd. today! Your satisfaction is our commitment.


