Plastic materials have become an integral part of everyday life, found in a wide range of applications, from packaging and construction to automobiles and electronics. When working with plastics, melting point is a crucial property, directly determining how the material can be processed and its end-use application. Understanding the melting point of plastic materials is crucial for product design and manufacturing.
This article will delve into the melting point of PVC plastic, providing a comprehensive guide by detailing its properties, different types, and how they affect processing and applications.
What is PVC plastic?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the world’s oldest and most widely used plastics. Made from salt (57%) and petroleum or natural gas (43%), it is the third-most produced synthetic plastic polymer globally, after polyethylene and polypropylene. PVC is used in a wide variety of household and industrial products, from raincoats and shower curtains to window frames and indoor plumbing. PVC is a lightweight, rigid plastic that can be made flexible by adding plasticizers.
What Is PVC Made Of?
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is primarily made from vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) through polymerization. During this process, additives such as plasticizers, stabilizers, and modifiers are added to enhance specific properties of PVC, such as flexibility and thermal stability.
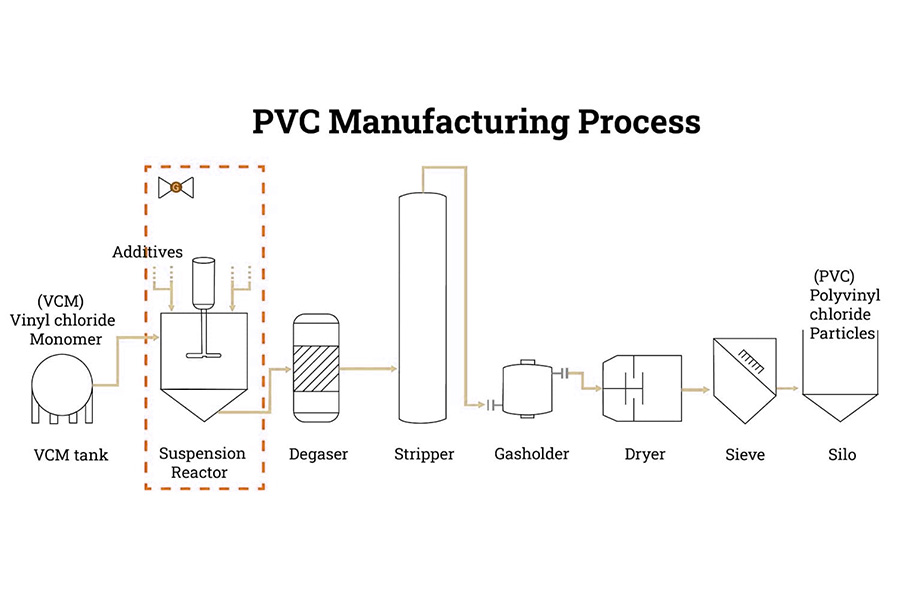
Comprehensive Analysis Of The Advantages And Disadvantages Of PVC Plastics
PVC plastic has wide acceptance across several industries, offering several benefits to these industries. However, like most materials used in production, PVC plastic has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of PVC
- Economical and Efficient: PVC is easily available, making it one of the most readily available and relatively inexpensive materials on the market.
- High Density and Rigidity: Its high density makes it very strong and more resistant to impact deformation than most plastics.
- Excellent Tensile Strength: It offers excellent resistance to abrasion and tearing, making it extremely durable.
- Good Chemical Resistance: Thanks to its amorphous nature, it is resistant to acids, alkalis, and a variety of chemicals.
- Flame Retardant: It is self-extinguishing due to its high chlorine content.
Disadvantages of PVC
- Poor Thermal Stability: Compared to other plastics, PVC has poor thermal stability and is prone to decomposition at high temperatures, requiring additives to improve its properties.
- Potential Toxicity: PVC can release fumes that are harmful to human health when exposed to fire or melted.
Common PVC Types: RPVC, Flexible PVC, CPVC Property Comparison
There are several types of PVC, each with specific properties and applications:
- Rigid PVC (RPVC, UPVC): Hard and inflexible, it’s often used in structural applications requiring strength and durability, such as building pipes, window frames, and doors.
- Flexible PVC (soft PVC): Flexibility is achieved through the addition of plasticizers and is used in cable insulation, flooring, medical tubing, inflatable products, and more.
- Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC): A chlorinated, modified form of PVC with increased heat and chemical resistance, it’s often used in hot water pipes, industrial systems, and fire sprinkler systems.
- Foamed PVC: A lightweight, rigid foam with a cellular structure, it’s used in signage, display panels, and insulation.
- Transparent PVC: A transparent material that allows light to pass through, it’s often used in clear pipes, windows, packaging, and display cases.
What Are The Characteristics Of PVC Plastic?
Electrical Properties: Excellent insulating material thanks to its excellent dielectric strength.
Durability: Weather-resistant, chemical-resistant, impact-resistant, and abrasion-resistant, making it a top choice for long-life and outdoor applications.
Flame Retardant: High chlorine content, self-extinguishing, with an oxidation index ≥45.
Cost-Effectiveness: Excellent physical and mechanical properties and excellent value for money, resulting in a long service life and low maintenance costs.
Mechanical Properties: Abrasion-resistant, lightweight, and tough.
Chemical Resistance: Resistant to all inorganic chemicals, with excellent resistance to dilute acids, alkalis, and aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Melting Point Temperature Of PVC Plastic
The melting point of PVC is a key property that affects its behavior and applications. But what exactly is the melting point of PVC? Simply put, it is the temperature at which PVC changes from solid to liquid.The melting temperature of PVC is not a fixed value. It can vary depending on the specific formulation of PVC, including the various additives used, such as stabilizers, fillers and lubricants. The composition of these additives can be very different, each affecting different properties of the final product.
The melting point of PVC is also affected by the isotacticity between the molecular chains. Syndiotacticity refers to the way PVC molecules are arranged in space, which affects how closely together the molecules are and therefore the temperature at which they begin to melt. The following is a explanation of the melting point temperature of PVC plastic:
| Attribute | Description |
| Material | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
| Melting Point | 100-260 °C (212–500°F) |
| Heat Stability | Low. PVC can decompose when overheated, producing harmful gases. |
| Additives and Their Effects | Heat stabilizers and plasticizers are often added to improve heat stability and flexibility. These additives significantly affect the melting point. |
| Decomposition Temperature | 140 degrees Celsius. At this point, PVC may begin to decompose and produce hydrochloric acid fumes. |
| Glass Transition Temperature | -20 to 80 degrees Celsius. This is the temperature at which PVC changes from a hard, glassy material to a rubbery one. |
| Effects of Melting Point | The melting point of PVC determines the processing temperature range. Too high can cause decomposition, while too low can cause insufficient fusion. |
| Importance of Controlling Melting Point | Proper control of the melting point is crucial for achieving desired material properties in the final product, including durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental conditions. |
Compared to other thermoplastics like polyethylene and polypropylene, PVC plastic exhibits a comparatively lower melting point. Its melting point typically ranges from 82°C to 260°C (180°F to 500°F) and may vary based on the specific grade and formulation used.For example, rigid PVC has a melting point of 185°F.
How To Compare The Main Polyvinyl Chloride Types?
| Mechanical Property | Rigid PVC (RPVC) | Flexible PVC | Chlorinated PVC (CPVC) | Foam PVC |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 45-75 | 10-20 | 55-80 | 5-15 |
| Young’s Modulus (GPa) | 2.5-3.5 | 0.02-0.04 | 2.5-3.5 | 0.02-0.04 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 10-40 | 200-500 | 50-100 | 200-400 |
| Minimum Service Temp. (°C) | -10 to 60 | -20 to 60 | -20 to 90 | -20 to 50 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.38-0.45 | 0.45-0.48 | 0.35-0.42 | 0.45-0.48 |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent | Opaque | Opaque |
What Is the Difference Between PVC And CPVC?
Chemical structure and properties
- PVC: It is a polymer polymerized from vinyl chloride monomer. It has an amorphous structure and its molecular formula is -(CH2-CHCl)n-. PVC itself has certain mechanical and electrical properties, but its heat resistance is poor, and the maximum operating temperature is generally around 80°C.
- CPVC: It is a product of PVC further chlorinated and modified. The chlorine content is generally 65%~72% (volume fraction). CPVC increases the irregularity and polarity of the molecular chain through chlorination, improving its chemical stability and heat resistance. The Vicat softening temperature of CPVC has been significantly increased, from 72-82°C of PVC to 90-125°C. The maximum use temperature can reach 110°C, and the long-term use temperature is 95°C.
Physical properties
- PVC: It has good mechanical properties, electrical properties and acid and alkali resistance, but poor heat resistance.
- CPVC: Not only inherits the excellent properties of PVC, but also has improvements in corrosion resistance, heat resistance, solubility, flame retardancy, mechanical strength, etc. CPVC’s physical properties such as density, Vicat softening temperature, tensile strength and flexural strength are better than PVC.
Application areas
- PVC: widely used in construction, wires and cables, packaging, medical equipment, household plastic products and other fields. Due to its low cost and good performance, PVC has a wide range of applications in the market.
- CPVC: Due to its excellent high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and flame retardant properties, CPVC is widely used in construction, chemical industry, metallurgy, shipbuilding, electrical appliances, textiles and other fields. Especially in piping systems, anti-corrosion coatings, electrical insulation materials, etc., CPVC performs well.
Preparation method and cost
- PVC: Prepared through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer, the cost is relatively low.
- CPVC: It is produced by chlorination modification on the basis of PVC. The preparation process is relatively complicated and the cost is high.
Factors Affecting The Melting Point Of PVC Plastic
The melting temperature of PVC plastic depends on several key factors, including:
- Chemical structure of polymers: Different types of plastics with different chemical structures will have different melting temperatures. For example, plastics with more hydrocarbon groups tend to have higher melting temperatures than plastics with different functional groups.
- Crystallinity: Crystalline plastics have a higher melting temperature than amorphous plastics. This is because the molecules in crystalline plastic are arranged in a specific order, making them less likely to break.
- Mass ratio of the components in the plastic: The melting temperature of the plastic is also affected by the mass ratio of its components.
- Additives: Additives added to a plastic can affect its melting temperature. For example, heat stabilizers can be added to increase the melting temperature of the plastic.
Common Uses Of PVC plastic
Construction: PVC plastic is used extensively in the construction industry for applications such as pipes, fittings, window frames, and flooring. PVC pipes are popular due to their low cost, lightweight, and excellent durability.
Packaging: PVC plastic is used in the packaging industry for applications such as blister packs, clamshells, and clear plastic containers. PVC plastic packaging is preferred due to its excellent clarity and toughness.
Automotive: PVC plastic is used in the automotive industry for applications such as dashboard components, door panels, and seat covers. PVC plastic is preferred for automotive applications due to its excellent durability and resistance to heat and cold.
Electrical: PVC plastic is used in the electrical industry for applications such as cable insulation, electrical conduit, and switch boxes. PVC plastic is preferred for electrical applications due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and low cost.
Medical: PVC plastic is used in the medical industry for applications such as blood bags, tubing, and catheters. PVC plastic is preferred for medical applications due to its excellent biocompatibility and ease of sterilisation.
Tips For Machining PVC Parts
There are many factors to take into consideration when machining PVC parts. Here, we provide helpful tips that would help improve the quality of PVC machined parts
Use The Right Cutting Tool
When machining PVC, making use of the right tool makes all the difference. PVC has stronger corrosive tendencies. So it is necessary to machine it with a cutting tool that is resistant to corrosion like stainless steel. This would help improve the precision as well as safety of the cutting process.
Setup Considerations
The way you set up your workspace also matters when machining PVC. Things to put into consideration include; machining speeds, bite angle, tooth counts, friction, and pressure. It is important you note that lower speed and force are ideal for machining PVC parts.
Prevent Contamination
When machining PVC parts, contamination is a serious concern, this is especially true where the part is for use in the aerospace and medical sector. One way to do this is to instantly clear chips away from the machined parts and use coolants the right way.
Drilling and Milling
When CNC milling PVC parts, using a high shear or high positive geometry cutter for face milling is ideal. On the other hand, for CNC drilling, it is best to use little downward pressure and slow to medium speed. Also, when drilling holes about ¼-inch or larger, choose bits or spade bits for drilling PVC plastics.
What Are the Commonly Used Processing Methods for PVC?
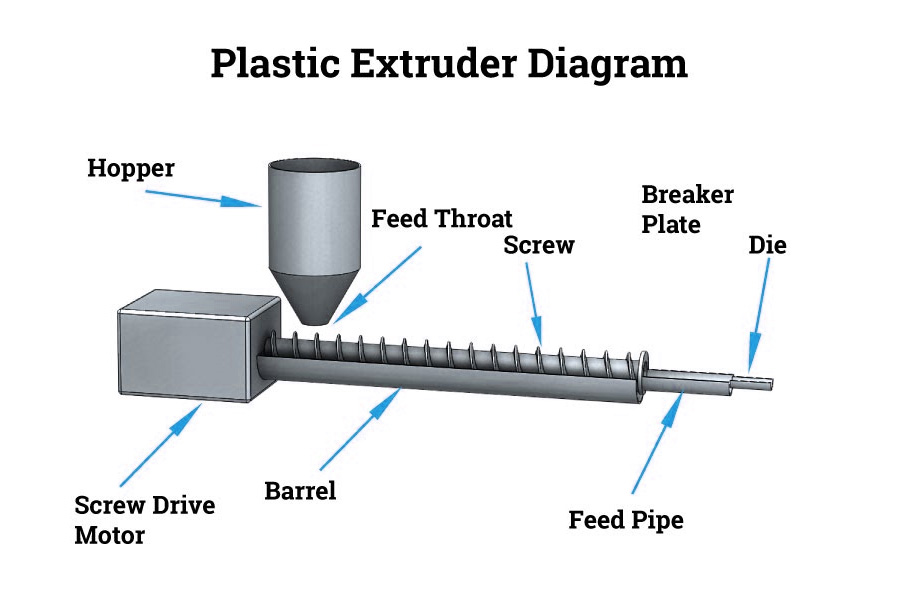
1.Extrusion molding
This is one of the most commonly used methods in PVC processing. Through the extruder, the PVC material is heated to a molten state, and then extruded through a die into products of the desired shape, such as pipes, plates, special profiles, etc.
2.Injection molding
Injection molding is to feed PVC particles into the barrel of the injection molding machine. After heating and melting, they are injected into the mold through high pressure. After cooling, the product of the desired shape is obtained. This method is suitable for producing various complex PVC plastic products, such as toys, containers, auto parts, etc.
3.Calendering
Calendering is to heat the PVC material to a certain temperature and then squeeze and stretch it through a series of parallel rollers to form a film or sheet. This method is often used to produce PVC films, floor leather, wallpaper and other products.
4.Blow molding
Blow molding is mainly used to produce PVC hollow products, such as bottles, containers, etc. During the blow molding process, the PVC material is heated and softened before being blown into shape through a mold.
5.Vacuum forming
Vacuum forming is to heat the PVC sheet to a certain temperature, use vacuum to adsorb it on the surface of the mold, and form a product of the desired shape after cooling. This method is often used to produce PVC decorative panels, billboards, etc.
6.Thermoforming
Thermoforming is a method in which PVC sheets are heated to a softened state and then shaped into the desired shape through pressure or vacuum. This method is suitable for producing PVC products with complex shapes.
7.Coatings and Cladding
PVC materials can also be used as coating or cladding materials. For example, PVC coatings can be used on fabrics, metal surfaces, etc. to provide waterproof, anti-fouling, wear-resistant and other properties.
LS: Meet all your plastic processing needs
Working with plastics, especially PVC, can expose you to certain risks. That’s why we generally recommend letting professionals like LS handle all of your plastic processing needs.At Longsheng, we provide diverse CNC machining services to manufacture top-notch plastic parts for customers around the world. We are able to produce high quality PVC machined parts using a wide range of different engineering plastics.
Additionally, we are an ISO 9001 certified factory and our quality control processes meet high standards. Do manufacturing of your plastic parts require tight tolerances and high precision? Rest assured, our CNC plastic machines can handle any job, regardless of complexity and plastic material. Simply upload your CAD file and get an instant quote!
Conclusion
PVC is an important plastic with a wide range of applications and diverse properties. Understanding its melting point range, thermal stability, and the differences between different types (such as PVC and CPVC) is crucial for making the right material selection and processing decisions.
In specific processes (such as injection molding), barrel temperatures are typically controlled between 170-190°C, and mold temperatures are maintained at 30-60°C using cooling water. While there is no fixed melting point, precise control of the melt temperature is crucial to successful processing. Therefore, choosing an experienced partner like LS is crucial to ensuring product quality.
FAQs
What is the density of PVC plastic?
Regarding the density of PVC, its specific values may vary due to different production processes, formulas and additives. But usually, the density of PVC is about 1.3~1.4 g/cm³. This range is based on the basic characteristics of PVC and common production processes.
What is the temperature resistance of PVC plastic?
The temperature resistance of PVC plastic is relatively weak, and its heat resistance is not strong. The softening temperature of PVC is roughly 80 to 85°C, that is, it starts to soften within this temperature range. At 130°C, PVC becomes viscoelastic. When the temperature reaches 160~180°C, PVC begins to transform into a viscos flow state. Soft PVC has lower temperature resistance and can usually withstand temperatures of 60°C. Rigid PVC has slightly higher temperature resistance and can withstand 70~90°C. Specially modified PVC can withstand higher temperatures, up to 100°C. In practical applications, appropriate PVC materials should be selected and corresponding usage strategies should be formulated based on the specific type and use of PVC, as well as the high temperature environment that may be encountered.
Which is more heat-resistant, PVC or PP (polypropylene)?
PP generally has better heat resistance than standard PVC. Homopolymer PP has a heat deformation temperature exceeding 100°C and a softening point of approximately 140-150°C, both higher than standard rigid PVC (~80°C). However, CPVC has better heat resistance than PP.
Is PVC plastic environmentally friendly?
PVC is not considered eco-friendly. It is made by a chemical reaction between chlorine, carbon, and ethylene and because it causes the release of other harmful chemicals, it does a lot of harm to the environment. In order to be transformed into a material that can be used in textiles or packaging, phthalates — which are plasticizers — are added, therefore adding another layer of harmful chemicals.
How to recycle PVC plastic?
There is mainly two ways to recycle PVC :①Mechanical recycling.This involves a mechanically treatment of the wastes. The PVC is grinded in small particles and cleaned. The particles can be then remelted and remolded with or without fresh material to redo same products or a new one.②Chemical recycling. Several chemical processes such as pyrolysis or hydrolysis are used to convert the waste into reusable components. The resulting products as sodium chloride, calcium chloride, hydrocarbon products can be used to produce new PVC or as feed for other manufacturing processes or fuel.
Resource
Properties and Application of Nanocrystalline Poly (vinyl chloride)
Effects of recycled PVC content and processing temperature on the properties of PVC foam products
LS Plastics Injection Molding Material Selection Guide
Advantages of Injection Molding in Industrial Manufacturing





