What’s the machine casting process?
Casting is a flexible and historic manufacturing process that entails pouring molten steel right into a mold to create a stable object with a selected form and construction. This process is key in producing a variety of merchandise throughout varied industries as a consequence of its skill to create advanced elements with intricate particulars and exact dimensions.
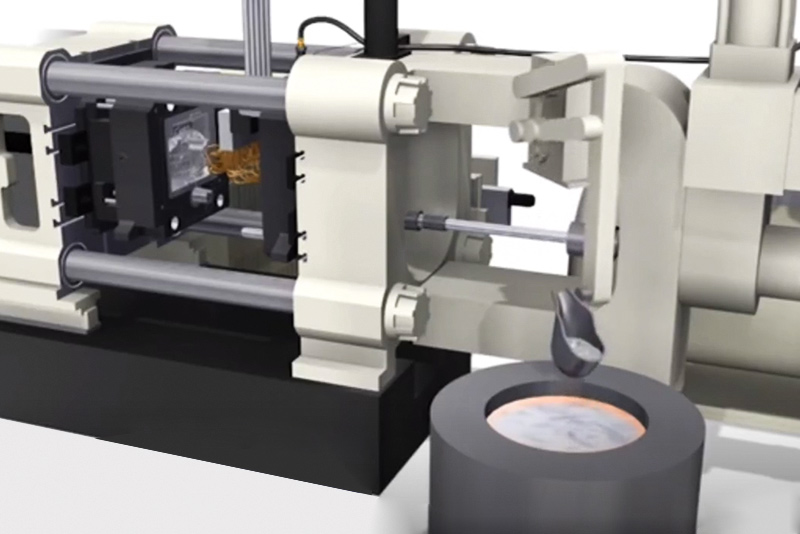

Forms of Casting Processes
Casting is a flexible manufacturing process that entails pouring liquid materials right into a mold to create a desired form. There are a number of kinds of casting processes, every with its personal benefits and downsides:
| Kind of Sample | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Free patterns | Single representations of the casting, normally produced in wooden. | Used when just a few castings are wanted. |
| Funding casting dies (Misplaced-wax) | Created from wax after which coated with a refractory materials. The wax is melted out, leaving a cavity for the molten steel. | Used for creating advanced and detailed shapes. |
| Break up patterns | Used to type a mould for casting uncommon shapes. Often made in two parts. | Used when the form to be solid is advanced. |
| Gated patterns | A number of free patterns having connected gates and runners. | Used for producing small castings in mass manufacturing methods and on molding machines. |
The primary perform of a casting sample is to mold a cavity within the molding sand combination such that the fashioned cavity appears the identical because the casting product. The number of materials for casting sample is dependent upon various factors such because the variety of casting, high quality of casting, and the diploma of end.
Past merely making a mold within the right form, sample design is integral to the event of a sound casting that is freed from casting defects. Since steel shrinks because it will get cooler, the sample needs to be designed to accommodate this shrink (also referred to as a shrinkage allowance). There are lots of design options wanted to efficiently accomplish this, corresponding to fillets, draft, and different strategies. Moreover, many inner options might be solid into the half.
The process of constructing a casting sample entails not solely shaping a mold cavity, but in addition contemplating correct dimensions, feeding system, and mold removing methodology. The casting patterns have to be designed in a method to improve the solidification and casting process reliability of the casting, prices associated to tooling and manufacturing are diminished, and stress concentrators are condensed.
Steps Concerned within the Casting Process
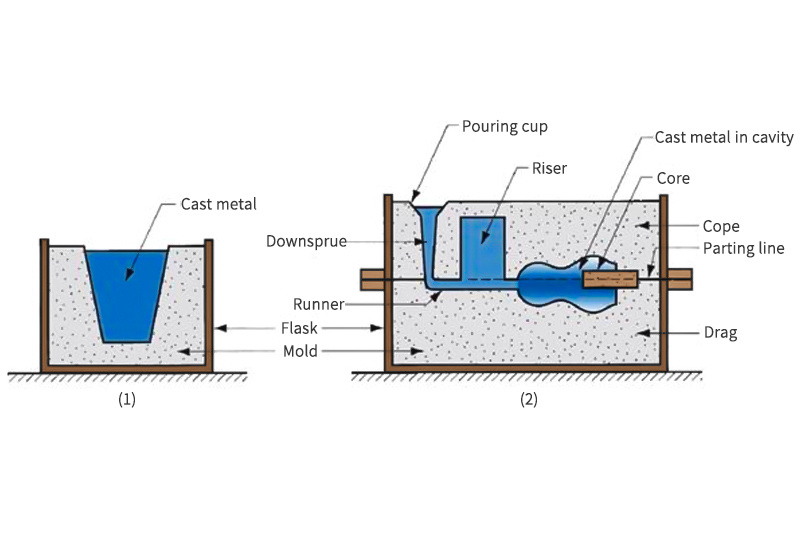
The casting process is a posh process that entails a number of steps. Here is a quick overview:
-
Sample Making: That is the preliminary step the place a sample, which is a reproduction of the thing to be solid, is created. This sample is used to type the mold cavity.
-
Mildew Making: The sample is then used to create the mold, which is often created from a cloth that may stand up to excessive temperatures. The mold is normally made in two halves, often known as the cope (high half) and the drag (backside half).
-
Clamping: To make sure stability in the course of the casting process, the 2 halves of the mold are clamped collectively.
-
Pouring: The steel, heated till it reaches a liquid state, is poured into the mold cavity.
-
Cooling: The molten steel is allowed to chill and solidify throughout the mold. The cooling time can fluctuate relying on the scale and thickness of the casting.
-
Ejection: As soon as the steel has cooled and solidified, the mold is opened and the casting is ejected, sometimes by knocking it out of the mold.
-
Cleansing and Inspection: The ultimate step entails cleansing and inspecting the casting. Any extra materials is eliminated, and the casting is inspected for defects.
Patterns in Casting
The casting process closely depends on patterns, that are basically replicas of the thing to be solid. These patterns are used to create the mold cavity, which is then stuffed with molten steel to provide the casting. The kind of sample used varies based mostly on the complexity and necessities of the casting.
Listed below are some widespread kinds of patterns:
-
Break up Piece Sample: This sample is split into two or extra parts and is used for advanced castings that can not be simply faraway from the mold.
-
Match Plate Sample: This sample has the cope and drag sections mounted on reverse sides of a plate, making it appropriate for top manufacturing runs.
-
Cope and Drag Sample: This two-part sample is utilized in sand casting, with the cope and drag as separate items.
-
Sweep Sample: Used for symmetrical and round shapes, a sweep is a bit of a contour rotated about an axis to create an entire sample.
-
Free Piece Sample: This sample consists of free items to create undercuts within the casting. These items are eliminated individually earlier than the mold is separated.
-
Gated Sample: Excellent for mass manufacturing, this sample entails a number of patterns related by a gating system, permitting for the simultaneous filling of a number of mold cavities.
Mould Preparation and Properties
The process of mold preparation is a vital facet of the casting process, because it instantly influences the form and high quality of the ultimate product. The steps concerned in mold preparation embrace sample placement, mold materials packing, sample removing, mold ending, creation of a pouring basin and runner, venting, and eventually, closing the mold.
The sample of the thing to be solid is first positioned in a flask, a field that holds the mold materials. The mold materials, usually a mix of sand and a binder, is then packed across the sample and compacted to make sure it holds its form. As soon as the mold materials has hardened, the sample is rigorously eliminated, leaving a cavity within the form of the thing to be solid. The mold cavity is then completed and inspected for proper form and measurement, with any obligatory corrections made at this stage. A pouring basin and a runner are created for the molten steel to be poured and attain the mold cavity, respectively. Vents are added to permit gases to flee in the course of the casting process, and eventually, the 2 halves of the mold (the cope and the drag) are assembled and securely clamped collectively.
mold for casting ought to possess sure properties, together with permeability, refractoriness, collapsibility, a clean floor end, hardness and energy, and in some circumstances, reusability. Permeability permits gases to flee in the course of the casting process to forestall defects, whereas refractoriness ensures the mold materials can stand up to the excessive temperatures of the molten steel with out breaking down. Collapsibility permits for simple removing of the casting after the steel has solidified. The mold cavity ought to have a clean floor to provide a superb floor end on the casting, and the mold must be laborious and robust sufficient to keep up its form and resist the erosive forces of the molten steel. In some casting processes, the mold materials must be reusable.
Core Making and Standards for Furnace Choice
The process of core making in casting is essential, significantly when coping with advanced shapes or inner cavities. A core, which is a preformed, bonded, sand insert, is positioned into the mold to form the inside of a casting or part of the casting that can not be formed by the sample. The core making process entails a number of steps:
- Core Field Making: A core field, a wooden or steel construction within the form of the specified core, is created.
- Core Sand Preparation: Core sand is ready by mixing sand with a binder and different components, which is then positioned into the core field.
- Core Hardening: The core sand combination is hardened, sometimes by baking it in a core oven at a selected temperature for a set time.
- Core Ending: After hardening, the core is faraway from the core field, and the surfaces are completed and inspected.
- Core Setting: The completed core is positioned into the mold cavity earlier than pouring the molten steel.
Relating to choosing a furnace for the casting process, a number of components must be thought-about:
- Kind of Steel: The furnace must be able to reaching and sustaining the required temperature for the steel being solid.
- Amount of Steel: The furnace measurement must be appropriate for the quantity of steel that must be melted.
- Gas Effectivity: The furnace must be fuel-efficient to attenuate operation prices.
- Ease of Temperature Management: The furnace ought to permit for simple and exact temperature management.
- Security: The furnace ought to have security options to guard operators and the atmosphere.
- Value: The price of the furnace, together with the preliminary buy worth, working prices, and upkeep prices, must be inside funds.
- Sturdiness and Reliability: The furnace must be sturdy and dependable, with a protracted service life and minimal downtime.
Defects and Prime quality Administration in Casting
Defects in Casting
Defects in casting signify undesirable abnormalities within the steel casting manufacturing process. These defects can happen throughout totally different levels of the process, together with molding, pouring, and cooling. A number of the widespread varieties of casting defects embrace:
- Fuel Porosity: This defect, which incorporates blowholes and pinholes, is brought on by gases equivalent to hydrogen getting trapped within the steel throughout the solidification process.
- Shrinkage Defects: These happen when the steel solidifies and shrinks, resulting in cavities or hole spots within the casting.
- Mould Materials Defects: These defects, which embrace cuts, washes, and steel penetration, are brought on by points with the mold materials or design.
- Pouring Steel Defects: These defects, which embrace chilly shuts and slag inclusions, happen resulting from issues throughout the pouring of the molten steel.
- Metallurgical Defects: These defects, which embrace scorching tears and scorching spots, are brought on by points associated to the metallurgy of the steel being forged.
- Casting Form Defects: These defects, which embrace warping and misalignment, have an effect on the form and dimensions of the ultimate casting.
High quality Administration in Casting
High quality administration in casting includes setting clear expectations and tolerances for high quality points with suppliers, in addition to implementing efficient inspection strategies to establish potential defects. A number of the key methods for high quality administration in casting embrace:
- Inspection: Casting inspection strategies are in place to make sure any hidden defects are recognized throughout the manufacturing process. These strategies can embrace each damaging and non-destructive testing.
- Prevention: Understanding the varied varieties of casting defects and their causes is vital to stopping these defects. This will contain enhancing the standard of the mold materials, optimizing the pouring process, and adjusting the metallurgy of the steel being forged.
- Correction: If defects are recognized, corrective actions must be taken to repair these points. This will contain repairing or changing the mold, adjusting the pouring process, or modifying the steel composition.
LongSheng Steel’s CNC Precision Machining Service
LongSheng Steel is certainly one of China’s high aluminum and zinc die casting manufacturing service suppliers. Along with casting, we additionally present prototyping, tooling, machining, and floor ending providers. We use essentially the most superior expertise for die-casting manufacturing. Our CNC machining service runs with one of the best expertise and a decade-long skilled engineers and employees. We provide one of the best cost-saving and technical machining design and manufacturing solutions you may ask for. Here’s a record of our CNC machining capabilities:- Our CNC milling store incorporates 5-axis CNC machines that are extremely exact. These machines are able to offering tolerance as much as 0.005mm.
- We now have speedy CNC fixture expertise that ensures quicker machining and on-time supply for our purchasers.
- Our machining service is just not just for casting parts but additionally for a lot of sorts of plastics and chrome steel parts.
- From superior CNC lathes and EDM machines to floor grinders and wire slicing machines, we’ve got every little thing you want for machining in our machine store.



The kindness that emanates from your blog is palpable, and it’s clear that it comes from a place of genuine passion.