Milling is a crucial metal cutting technique in manufacturing that accurately shapes the desired shape and size of the parts by using rotating milling cutters to remove excess material from the workpiece. Milling is usually performed on milling machines, and the flexibility and high accuracy of such machine tools makes milling an integral part of the manufacturing industry.
In this guide, I will lead you to learn the definition of milling, principle, process, type, advantages and disadvantages, application scope and what is turning. Finally, through the comparison of the two, choose the processing method suitable for you.
What’s Milling?
Milling is the method of machining utilizing rotary cutters to take away materials by advancing a cutter right into a workpiece. This course of could also be finished by various instructions on one or a number of axes, cutter head pace, and strain. Milling covers all kinds of various operations and machines, on scales from small particular person parts to giant, heavy-duty gang milling operations. It is without doubt one of the mostly used processes for machining customized parts to specific tolerances.
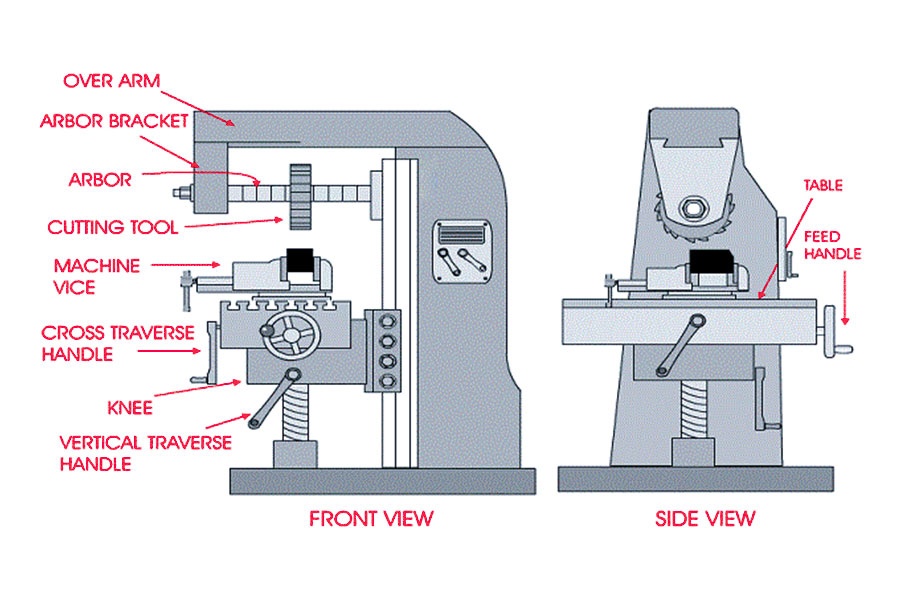
What is the principle of milling?
Movement of the cutting tool and the workpiece
During the milling process, the tool rotates at a high speed through the main shaft, forming the main motion. At the same time, the workpiece moves relative to the tool, which is called feed movement. The workpiece can also be fixed, when the tool needs to complete both the main and feed movements.
The role of cutting force
When the cutting part of the tool contacts with the surface of the workpiece, it will produce the cutting force, which is the key to remove the surface material of the workpiece. The size of the cutting force is related to many factors, including the number of cutting blades, blade angle, rotation speed, feed speed, cutting depth and other parameters.
Material removal
Under the action of cutting force, the cutting edge of the tool cuts along the surface of the workpiece to gradually remove the excess material on the workpiece. The cutting process can be performed on multiple surfaces of the workpiece, and the tool can be moved on three axes to achieve this.
Processing parameters
Important parameters in the milling process include the cutting speed, feed speed, and cutting depth. Cutting speed is the average linear speed of the tool relative to the surface of the workpiece, which determines the rate of material removal. The feed speed refers to the feed amount of the tool in unit time, which affects the roughness and machining efficiency of the machining surface. Cutting depth is the depth of the workpiece at each cutting time, which determines the amount of material removed at each cut.
Machining effect
By adjusting the above parameters, the machining effect of milling can be controlled, including machining accuracy, surface roughness, machining efficiency, etc.
Reasonable selection of cutting parameters and tool type can achieve high precision control of work piece shape and size.
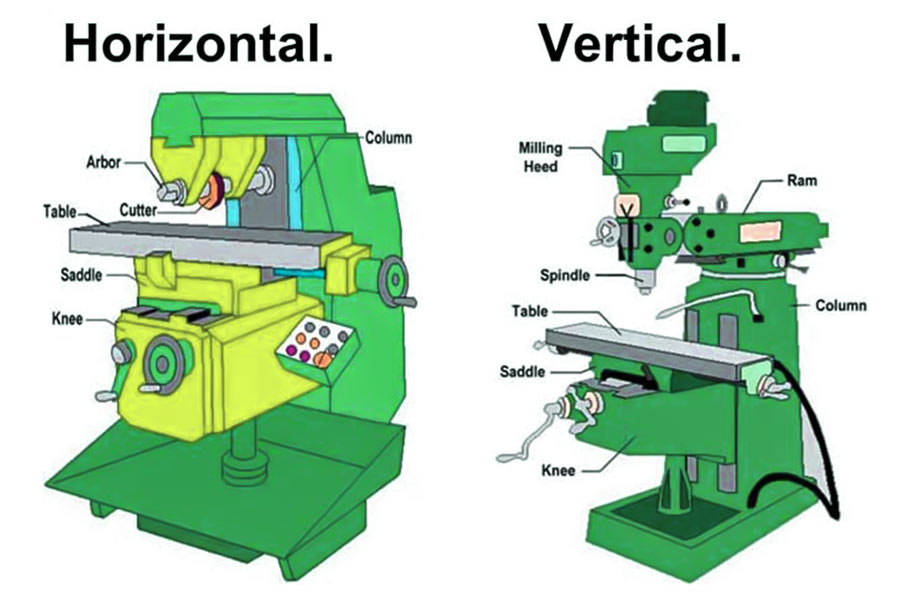
Milling bed type
Milling is usually performed on milling machines, and there are many types of milling machines, such as horizontal milling machine, vertical milling machine, gantry milling machine, etc. These milling machines are suitable for processing tasks of different sizes and complexity, and are indispensable equipment in modern manufacturing industry.
In short, the basic principle of milling is to gradually remove the excess material on the workpiece under the action of cutting force through the relative movement between the rotating tool and the workpiece, so as to realize the high precision processing of the shape and size of the workpiece. By adjusting the cutting parameters and selecting the appropriate tool type, the machining effect can be controlled and different machining requirements met.
Process flow of the milling process
The milling process can be clearly divided into the following steps, each of which includes key operations:
| process flow | key operations |
| Design product drawings | Based to the product requirements using computer-aided design software (such as CAD). The dimensions and positions of the holes and grooves to be milling are clearly marked on the drawings. |
| Select the cutting tool | Select the appropriate milling cutter head according to the material and processing requirements of the product. For example, for the aluminum alloy material, the rigid carbide thread drilling and milling cutter can be selected. |
| Design the cutting path | Determine the cutting path and processing sequence according to the product drawings. This helps to optimize the processing process and improve the processing efficiency. |
| Set the machine tool parameters | Set the appropriate cutting speed, feed speed and cutting depth according to the material hardness and product requirements. For example, for aluminum alloy materials, the milling cutter speed can be set to 2,000 r/min, the cutting speed is 314m / min, the milling feed is 0.06mm / tooth, etc. |
| Install the workpiece | Attach the workpiece to be processed on the milling machine to ensure stability and positioning accuracy. This can be achieved by using fixtures or other tooling equipment. |
| Processing operation | After the workpiece is stable and the machine parameters are set correctly, start the machine and start milling. In the processing process, it is necessary to closely monitor the cutting situation and timely adjust the cutting parameters to ensure the processing quality. |
| Processing inspection | After milling, inspect the finish surface. This includes dimensional inspection, surface quality inspection, etc. to ensure that the processing quality meets the requirements. |
| post processing | If a problem is found in the processing inspection, improve or grind accordingly until the requirements are met. |
Precautions in the milling process
- Choose the right tool: according to the processing materials and workpiece size and other factors, choose the right milling cutter, to ensure the processing accuracy and processing efficiency.
- Adjust the cutting parameters: according to the machining requirements, adjust the cutting depth, cutting speed and motion mode of the milling cutter to ensure the machining accuracy and machining efficiency.
- Keep the correct operation of the machine tool: in the machining process, ensure the correct operation of the machine tool to ensure that the cutter has sufficient cutting force and the accuracy of the workpiece.
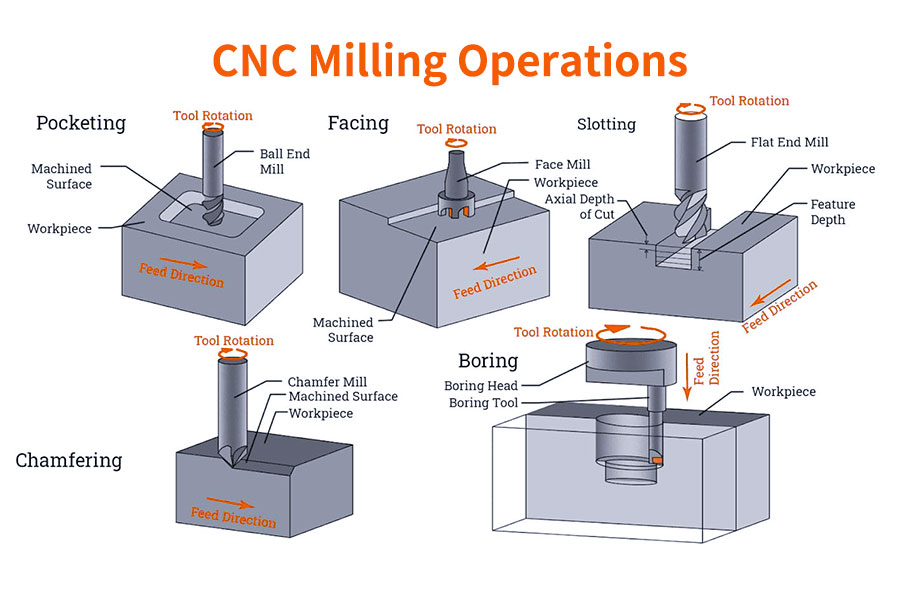
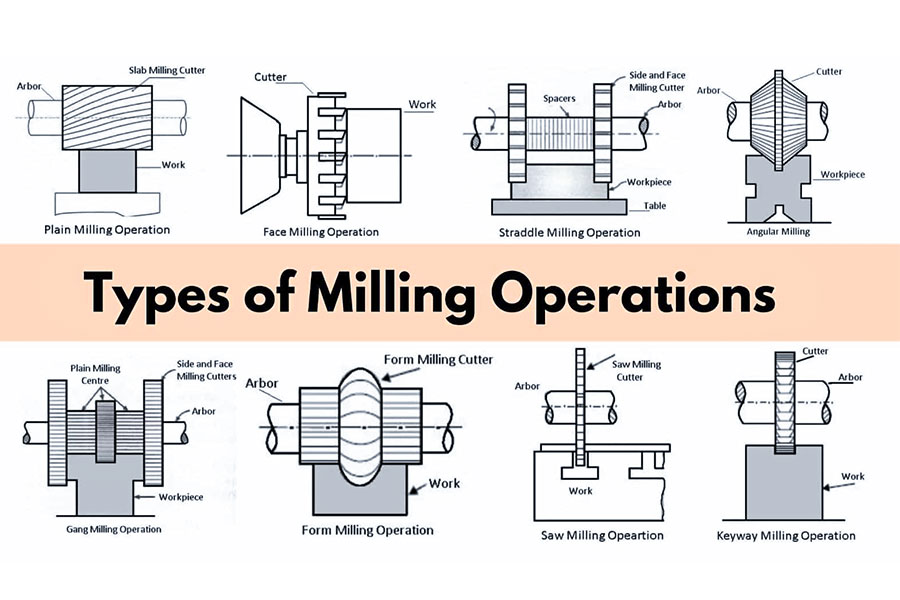
What are the types of milling?
Primarily based on the search outcomes, the sorts of milling operations embody:
- Plain Milling: Includes the creation of a flat horizontal floor parallel to the cutter’s axis utilizing a plain milling cutter.
- Face Milling: Produces a flat floor perpendicular to the cutter’s axis.
- Finish Milling: Produces slots and pockets.
- Turret Milling: Makes use of a turret mill for varied milling operations.
- Horizontal Milling: Holds and rotates the spindle within the horizontal orientation to take away materials from the floor of a stationary workpiece.
- Vertical Milling: Removes materials from flat and vertical surfaces of a workpiece.
- Common Milling: Gives versatility in machining operations and may carry out each vertical and horizontal milling.
- Dro Milling: Makes use of a digital readout (DRO) system for exact milling operations.
- CNC Milling: Managed by a pc numerical management system and a G-code program, permitting for broad functionality machining.
- Tracer Managed Milling: Includes the usage of a tracer to regulate the milling operation.
- Omniversal Milling: Supplies a variety of machining capabilities for varied milling wants.
- Profile Milling: Used for creating advanced shapes and profiles on the workpiece.
- Planetary Milling: Includes the usage of planetary movement for milling operations.
- Drum Milling: Makes use of a drum milling machine for particular milling necessities.
- NC/CNC Milling: Incorporates numerical management for exact and automatic milling operations.
Advantages of milling
| Advantages | Options |
| Wide used | Milling is a widely used process. It can create various shapes on many different types of materials. Alternative manufacturing processes such as 3D printing are limited with regard to materials. |
| Accuracy | CNC milling is one of the most accurate manufacturing techniques. It is the preferred process in areas such as aerospace, because the precision in these areas is crucial. |
| Efficient | Milling is very efficient. CNC milling can rapidly manufacture parts and are suitable for mass production. |
| Quality | Milling is a high-quality process. Milled parts usually do not require a secondary surface finish. |
| Automation | Milling is usually integrated with CNC machine tools. This automates the entire process, reducing labor demand and increasing productivity. |
| Cost-effective | High productivity and low labor costs make operations very cost-effective. |
| Consistency | The high precision of milling can produce very consistent parts. This is very important for making commercial parts that are key to reproducibility. |
| Processing hard materials | Milling can easily process hard materials such as titanium and Inkoner. These materials are very difficult to process with alternative techniques. |
Disadvantages of milling
| Disadvantages | Options |
| Material Wastage | CNC milling follows a subtractive manufacturing approach, where a block of material is shaped by removing portions to create the final part. Due to this method, CNC milling generates more material wastage compared to additive manufacturing processes like 3D printing, which build parts layer by layer without significant material loss. |
| Initial Investment Cost | CNC milling machines can be expensive to purchase and set up, especially high-quality and advanced models. The initial investment can be a significant barrier for small businesses or individuals. |
| Complexity and Training | Operating and programming CNC milling machines require specialized skills and training. Skilled operators and programmers are essential to ensure smooth operations and accurate results. The learning curve can be steep, adding to the overall cost and time investment. |
| Maintenance and Downtime | Regular maintenance is essential to keep the machines running efficiently and accurately, involving tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and component inspection. Proper calibration and alignment are necessary to maintain precision. Downtime, on the other hand, refers to the period when the machine is not operational due to maintenance, repairs, or unexpected breakdowns. Unplanned maintenance or breakdowns can result in costly downtime, impacting production schedules. |
| Software and Programming Errors | Errors in programming or software issues can lead to mistakes in machining, resulting in scrap parts and wasted materials. Proper verification and simulation are crucial to minimize such errors. |
What materials are commonly used for custom milling?
Aluminium
Aluminum is a widely used metal material with light weight, high strength, easy processing and good corrosion resistance. Aluminum has a density of about 2.7g / cm³, only a third of copper and steel, but the strength is very high. Moreover, aluminum has excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, so that it is widely used in electric power, electronics, heat exchanger and other fields.
There are many kinds of common aluminum alloy and its common aluminum alloy, such as 2024,5052,6061,7075 and so on.2024 aluminum alloy high strength, good fatigue resistance, often used in aircraft structure; 5052 aluminum alloy good corrosion resistance, often used in the manufacture of oil tank, pipe, etc.; 6061 aluminum alloy welding, processing, often used in the manufacture of body structure; 7075 aluminum alloy high strength, often used in manufacturing high strength parts.
Steel
A variety of steel alloys can be used for CNC processing. Steel alloy can be selected if parts require higher formability and greater weldability, such as gears, shafts, or certain high-stress applications. Stainless steel, low carbon steel, alloy steel and tool steel are the main types of CNC steel. Stainless steel is highly recommended when parts require high strength, high ductility, excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance. In addition, stainless steel has good workability and is easy to weld and polish. Low carbon steel (low carbon steel) is appropriate when the cost plays an important role and the application is for general use. Carbon steel also has good weldability and corrosion resistance. Alloy steel and TiSCO are the exceptions when you consider higher hardness, greater stiffness, and heat resistance.
Copper
Copper is a popular CNC processing material with unique properties, including excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. Because to its excellent electrical conductivity, product engineers consider copper and its alloys ideal for electrical and electronic components. Similarly, copper alloy is the perfect CNC material for jewelry production because of its excellent beauty. Wire, jewelry production, and magnetic equipment are typical applications of copper.
Brass, bronze and copper are indispensable for CNC processing materials. Brass and bronze are common copper alloys with unique properties. Brass is composed of copper and zinc. It is a very soft metal that can be processed without lubrication. It has excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance and workability. Manufacturers often use brass for applications that do not require high strength, such as the manufacture of low-strength fasteners, electrical equipment, consumer goods, and piping equipment.
Bronze, on the other hand, consists of copper, tin, and other composite elements. It is strong and durable, and has a strong corrosion resistance. Bronze has excellent workability, which is perfect for machining precision parts such as bearings and gears. In addition, the addition of aluminum and phosphorus can improve the impact resistance, toughness, and strength of bronze.
Titanium
This CNC metal is very strong and light in weight, with an excellent strength to weight ratio. The corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity and biocompatibility of titanium make it compatible with CNC processing in the biomedical industry. Titanium is compatible with welding, passivation and anodizing processes for enhanced appearance and protection. Although titanium has poor electrical conductivity, it has good thermal conductivity and high melting point.
In addition, titanium is well suited for manufacturing high-performance mechanical parts in the medical, military, aerospace and automotive industries. More noteworthy, titanium is suitable for manufacturing cutting tools for CNC machine tools.
Plastics
Plastics are also very popular option for CNC machining because of its wide choices, relatively lower price, and significantly faster machining time needed.According to different characteristics and uses, plastics are divided into many species, such as POM, ABS, PVC, etc. Plastics are characterized by small density, high strength and strong plasticity, and are widely used in electronics, automobile manufacturing, environmental protection and other fields.
Ceramic
Ceramics is another common non-metallic material, with the advantages of high strength, high hardness, high wear resistance, corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance. Among them, alumina ceramics, silicon nitride ceramics, silicon carbide ceramics and other types are common in industrial manufacturing, electronics, aerospace and other fields.
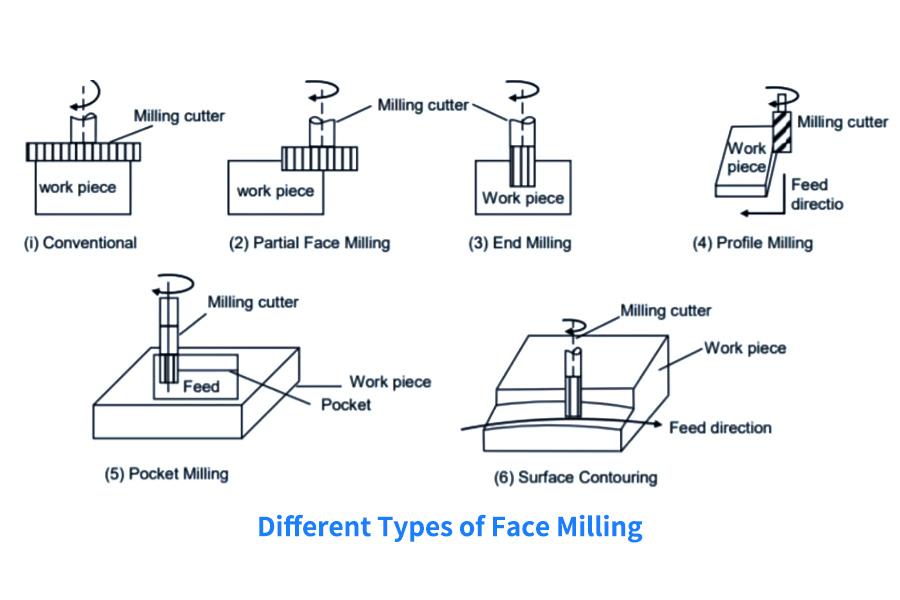
The application range of the milling process
CNC milling has a wide range of applications across various industries, thanks to its versatility and precision. Some of the key applications of it include:
Aerospace
CNC milling is extensively used in the aerospace industry to manufacture complex components for aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft. It allows for the production of lightweight and high-strength parts like turbine blades, engine components, structural elements, and landing gear.
Medical
In the medical field, CNC milling is used to fabricate medical implants, surgical instruments, prosthetics, and other medical devices. The ability to create customized and patient-specific parts is particularly beneficial in this industry.
Automotive
CNC milling is essential in the automotive manufacturing industry for producing engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission components, and other intricate parts. It enables automotive manufacturers to achieve high precision and consistency in their products.
Electronics
CNC milling is employed to manufacture printed circuit boards , which are essential components in electronic devices. It allows for precise routing, drilling, and milling of PCBs, ensuring the accuracy of electrical connections.
Mold Making
CNC milling is widely used in the creation of molds for plastic injection molding, die-casting, and other molding processes. The ability to produce intricate and precise molds leads to high-quality finished products.
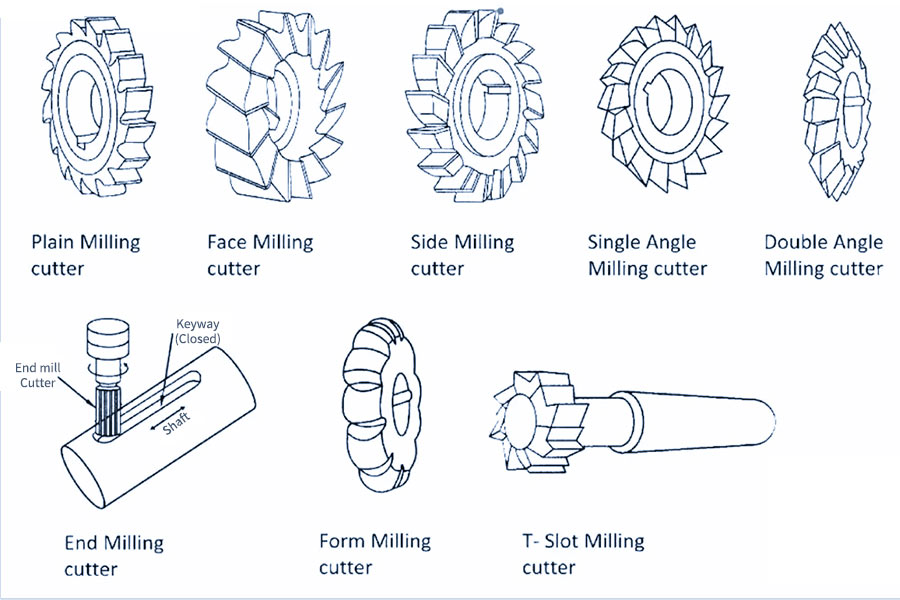
What is turning?
turning is a manufacturing process that involves the use of computer-controlled machines to create precise and complex parts. During turning, a workpiece is rotated while a cutting tool removes material from the workpiece to create the desired shape.
What is the Working Principle of Turning?
Turning operates on a simple yet effective principle:
- The workpiece is rotated at high speed while a single point cutting tool traverses along the workpiece’s surface, cutting off a thin layer of material.
- The cutting action takes place at the point where the tool’s cutting edge meets the workpiece.
- This cutting speed, coupled with the feed rate (the speed at which the cutting tool moves relative to the workpiece), determines the shape and surface finish of the final product.
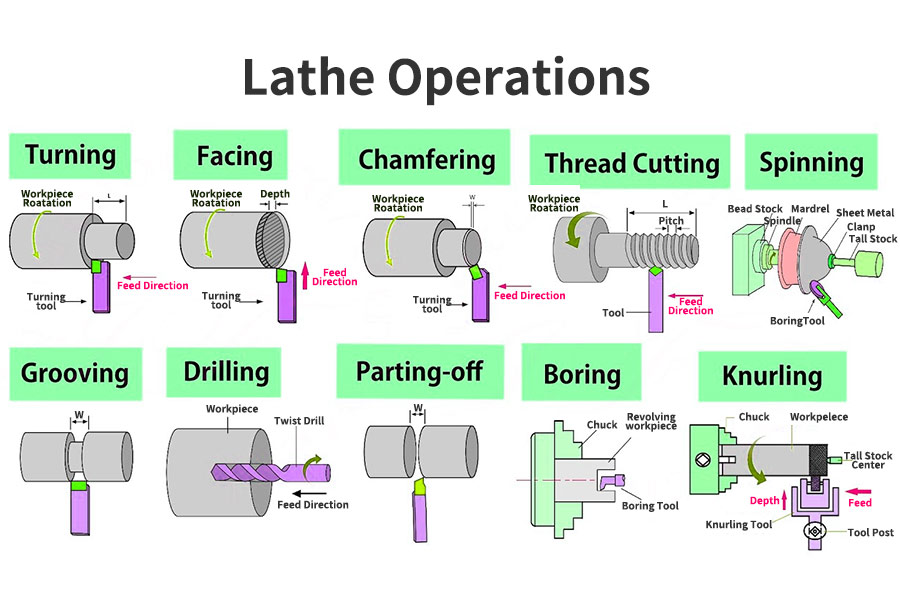
What are the types of turning ?
- Straight Turning: Straight turning involves the removal of metal from the external surface of a cylindrical workpiece. The cutting tool moves longitudinally along the workpiece, reducing its diameter. It is often used to ensure cylindrical workpieces have a consistent diameter along their length.
- Taper Turning: In taper turning, the tool is not parallel to the axis of the lathe, but at an angle, allowing for the creation of conical shapes. This technique is commonly used to create machine tool spindles and drive shafts that require a tapered end for fitting components.
- Facing: This operation involves reducing the length of a workpiece or creating a smooth end or face. The cutting tool moves radially across the end of the workpiece, removing material. It’s used frequently to clean up the ends of parts or prepare surfaces for additional machining processes.
- Groove Turning : This type involves cutting a narrow groove on the external or internal surface of the workpiece. Groove turning is commonly used for oil grooves, retaining ring grooves, and for parting off sections of a workpiece.
- Parting: Parting or cutoff is the operation of cutting off a piece from a larger workpiece. It involves the creation of a narrow slot down to the center of the workpiece, ultimately separating a section of material. It is typically the final operation after the part is fully shaped.
- Thread Turning: This type involves cutting a helical groove of a particular pitch along the external or internal surface of a cylindrical workpiece. Thread turning is used to make screw threads for fasteners and other components requiring threaded features.
- Boring: Boring is the process of enlarging a hole that has already been drilled or cored. It can improve hole accuracy and provide a smooth internal surface. It’s used for finishing internal surfaces or preparing them for additional operations like thread turning.
- Knurling: This operation produces a regularly shaped roughness on the workpiece surface, often to provide a better grip for handling. The knurling tool presses a pattern into the surface of the workpiece as it rotates.
- Drilling: In a lathe, drilling is the operation of making a cylindrical hole by removing metal along the circumference of a pointed tool or drill bit. It’s typically the first step in creating an internal feature that will be further refined by operations like boring or thread turning.
- CNC Turning: CNC turning employs computer programs to control the cutting tool’s motion. It enables the creation of complex parts at high speeds and with high precision. CNC turning is particularly useful for producing parts with complex radial features or when tight tolerances are required.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Turning
The advantages of turning include:
- Efficiency in mass production due to automation
- High level of precision and accuracy
- Ability to handle complex shapes and geometries
- Provides a good surface finish
On the other hand, the disadvantages are:
- Initial setup can be time-consuming
- Less efficient for non-cylindrical or complex shaped parts
- Operator skill and experience play a critical role
- The process may require frequent tool changes due to tool wear.
Milling vS Turning
| Milling | Turning | |
| Method | Rotates cutting tool at pre-set RPM | Rotates workpiece at pre-set RPM |
| Result | Flat or sculptured | Cylindrical or conical |
| Machine | Milling machine | Lathe |
| Tool | Multi-point cutting tool | Single point turning tool |
| Contact | Cutting tool cuts intermittently during operation | Cutting tool remains in continuous contact withworkpiece during operation |
| Movement | Workpiece moves | Cutting tool moves |
| Waste | Produces discontinuous chips | Produces fragmented,discontinuous, or continuouschips |
How to choose between milling and turning?
If you need to process the workpiece with a rotary surface, and the machining accuracy and efficiency have high requirements, then turning is a better choice.
If a complex shape such as machining plane, groove, forming surface, or the processing of complex shapes and features are required, then milling is a better choice. In addition, milling has a long tool life when processing difficult materials.
Tips for choosing a milling company
Corporate expertise and reputation
The first thing to consider when choosing a milling company is the company’s expertise and reputation. Professional companies like Longsheng can usually offer higher quality services because they have the knowledge and experience of handling a variety of complex milling tasks. Also, the company’s reputation is important because it reflects the quality of their work and customer satisfaction. Longsheng is known for its good reputation and high quality service.
Tools and Tricks
The tools and technologies used by companies are also important considerations. Companies like Longsheng that use the latest tools and technologies can often provide more accurate and efficient milling services. Furthermore, they are more likely to handle a variety of complex milling tasks.
Service and assistance
Excellent customer service and support are also important factors in choosing a milling company. Companies like Longsheng that provide excellent customer service can ensure that they meet your needs and help with problems. In addition, they also offer personalized solutions to meet your specific needs.
Value and supply time
Finally, price and delivery time are also factors to consider. It is best to choose a company that can provide reasonable prices and fast delivery time, such as Longsheng. Remember, however, that quality and service are often important, so don’t make decisions based on price alone.
Conclusion
Milling is a widely used in modern manufacturing, has different requirements and characteristics for different materials. Correct selection of cutting tools and parameters, master the milling skills and matters needing attention, can improve the processing efficiency and quality, to meet the processing needs of different materials.
Longsheng is a company specializing in providing CNC milling services, with many years of industry experience and advanced equipment. We are familiar with various processing materials and processes, and can provide customized solutions according to customer needs. Whether it is small batch production or mass production, we can ensure the product quality and delivery time, to make the customer satisfaction, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to helping you and being your preferred partner.
FAQs
How to choose the right milling cutter when milling?
The selection of a suitable milling cutter requires a comprehensive consideration of the processing requirements, milling cutter type, parameters, blade material and coating, cutting methods and conditions, cutting stability and cost, and tool power and tool size. In practical application, it may also need to test and adjust according to the specific situation to achieve the best processing effect.
How much does the milling process cost for?
Milling processing cost is a complex problem involving a comprehensive consideration of multiple factors. No fixed value, when quotation need to consider many aspects, such as labor cost, fixed cost, accuracy, processing, raw materials, heat treatment, surface treatment and pretreatment, machinery, outsourcing processing, auxiliary materials, labor and electricity, processing in the process of transportation, finished product inspection and nondestructive testing, material testing, as well as reasonable profit, reasonable distribution, mold cost of reasonable apportionment, freight, taxes, etc.
What is the golden rule of milling?
The golden rule of milling is thick in and thin out. When the tool enters the workpiece, the operator shall aim at the thick chips. During the subsequent operation and tool exit from the workpiece, the operator shall aim for thinner chips. This enables stable milling operations.
How accurate is the milling process?
Milling is one of the most accurate manufacturing processes available. It can provide a tolerance of as low as ± 0.005 inches.
What’s the difference between milling and 3D printing?
There are many differences between milling and 3D printing. Milling is a material-reduction manufacturing technique. On the other hand, 3D printing is an additive manufacturing technique. Milling is suitable for all materials, but 3D printing is the only case for certain plastics.



